Are you struggling with resolving SSL protocol errors? In this article, we will guide you through three easy steps to fix this issue.
Understanding ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR
To resolve ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR, follow these 3 easy steps:
1. Check your system clock: Make sure your computer’s clock is set correctly. An incorrect system time can cause SSL protocol errors. Adjust the time and date settings in your operating system’s control panel.
2. Clear browsing data: Clear your browser’s cache, cookies, and history. These stored data can sometimes interfere with the SSL handshake process. In Google Chrome, go to Settings > Privacy and security > Clear browsing data. In Firefox, go to Options > Privacy & Security > Clear Data.
3. Disable antivirus software: Temporarily disable any antivirus or firewall software that may be blocking the SSL connection. Check the settings of your antivirus program and disable any SSL scanning or HTTPS inspection features. Remember to enable the antivirus software after resolving the SSL error.
If you’re still experiencing the SSL protocol error after following these steps, consider updating your browser to the latest version or contacting your web hosting service for assistance.
Video Tutorial: How to Fix
Step 1: Clear your browser cache.
– Open your web browser’s settings or options menu.
– Locate the “Clear browsing data” or “Clear cache” option.
– Select the appropriate time range and check the “Cache” or “Temporary files” box.
– Click on the “Clear” or “Delete” button.
Step 2: Update your browser.
– Open your web browser and go to the settings or options menu.
– Look for the “About” or “Help” section.
– Click on the “Check for updates” or “Update” button.
– Follow the prompts to install any available updates.
Step 3: Adjust your security settings.
– Open your web browser and go to the settings or options menu.
– Look for the “Privacy” or “Security” section.
– Disable any browser extensions or add-ons that may be interfering with the SSL protocol.
– Reset your browser’s security settings to the default or recommended values.
Common Causes Identified
- Open your web browser
- Access the browser settings menu
- For Chrome: Click on the three-dot icon in the top right corner, then select “Settings”
- For Firefox: Click on the three-line icon in the top right corner, then select “Options”
- For Safari: Click on “Safari” in the top menu, then select “Preferences”
- Navigate to the “Privacy” or “Security” section
- Find the option to clear browsing data
- For Chrome: Click on “Clear browsing data” or “Advanced” > “Clear browsing data”
- For Firefox: Click on “Privacy & Security” > “Clear Data”
- For Safari: Click on “Privacy” > “Manage Website Data”
- Select the items you want to clear
- Make sure to check “Cached images and files” or similar option
- Click on “Clear” or “Clear Data”
- Restart your browser
Repair Method 2: Update Browser
- Determine which browser you are using
- Visit the official website of your browser
- Look for the “Download” or “Update” button
- Click on the button to download or update the browser
- Follow the on-screen instructions to install the update
- Restart your computer
Repair Method 3: Disable Antivirus or Firewall
- Open your antivirus or firewall software
- Access the settings or preferences
- Look for options related to SSL or HTTPS scanning
- Disable the SSL or HTTPS scanning feature
- Save the changes and close the software
- Restart your computer
Step 1: Verify SSL Certificate Installation
To resolve the SSL Protocol Error, the first step is to verify the installation of the SSL certificate. Here’s how you can do it:
1. Open your web browser (such as Microsoft Edge or Google Chrome) and visit your website.
2. Look for the padlock icon in the address bar. This indicates that the SSL certificate is installed correctly. If you see a warning or an error message instead, proceed to the next step.
3. Check the certificate details by clicking on the padlock icon. Look for information such as the certificate issuer, the validity period, and the subject alternative name (SAN).
4. Verify the certificate chain by checking if all the intermediate certificates are properly installed. This ensures that the certificate is trusted by the browser.
5. Use an online SSL checker tool to validate your certificate installation. These tools will provide a detailed report on the certificate’s validity and any potential issues.
6. If you’re using a wildcard certificate or a certificate with multiple domains, make sure that all the subject alternative names are included and correctly configured.
7. If you’re unsure about the SSL certificate installation, contact your web hosting service or the certificate provider (such as Domain.com or GoDaddy) for assistance.
By verifying the SSL certificate installation, you can ensure that your website is secure and free from SSL protocol errors. This step is essential for building trust with your users and protecting their sensitive information.
Step 2: Ensure Correct SSL Configuration
1. Check the SSL certificate installation. Verify that the public key certificate is properly installed on the server. This ensures secure communication between the server and the client.
2. Verify the SSL handshake. The handshake is a crucial step in establishing a secure connection. Ensure that the handshake process is completed successfully without any errors.
3. Check for compatibility issues. Some browsers or applications may have compatibility problems with certain SSL configurations. Verify if the SSL configuration is compatible with the client’s browser or application.
4. Test the SSL connection. Use a browser extension or an online SSL checker tool to verify the SSL configuration and check for any errors or warnings.
5. Troubleshoot any SSL protocol errors. If you encounter an SSL protocol error, refer to the specific error message and troubleshoot accordingly. Check for any misconfigurations, incorrect settings, or missing components.
6. Update SSL configuration if necessary. If any issues are detected, update the SSL configuration based on the recommended settings or guidelines provided by your SSL certificate provider.
Step 3: Update Expired SSL Certificates
To update expired SSL certificates, follow these 3 easy steps:
Step 1: Identify the expired SSL certificates
– Access your server or hosting provider’s control panel.
– Look for the SSL certificate section or a similar option.
– Locate the expired certificate(s) and make note of their names.
Step 2: Generate new SSL certificates
– Visit a trusted SSL certificate provider like Domain.com or GoDaddy.
– Select the type of SSL certificate you need (e.g., wildcard or subject alternative name).
– Enter the required information, such as your domain name and organization details.
– Complete the purchase and follow the provider’s instructions to generate the new certificate(s).
Step 3: Install the new SSL certificates
– Go back to your server or hosting provider’s control panel.
– Find the SSL certificate section again.
– Choose the option to install a new certificate.
– Upload the new certificate files that you obtained from the SSL provider.
– Save the changes and ensure the new certificates are properly installed.
Clearing Browser Data and Cache
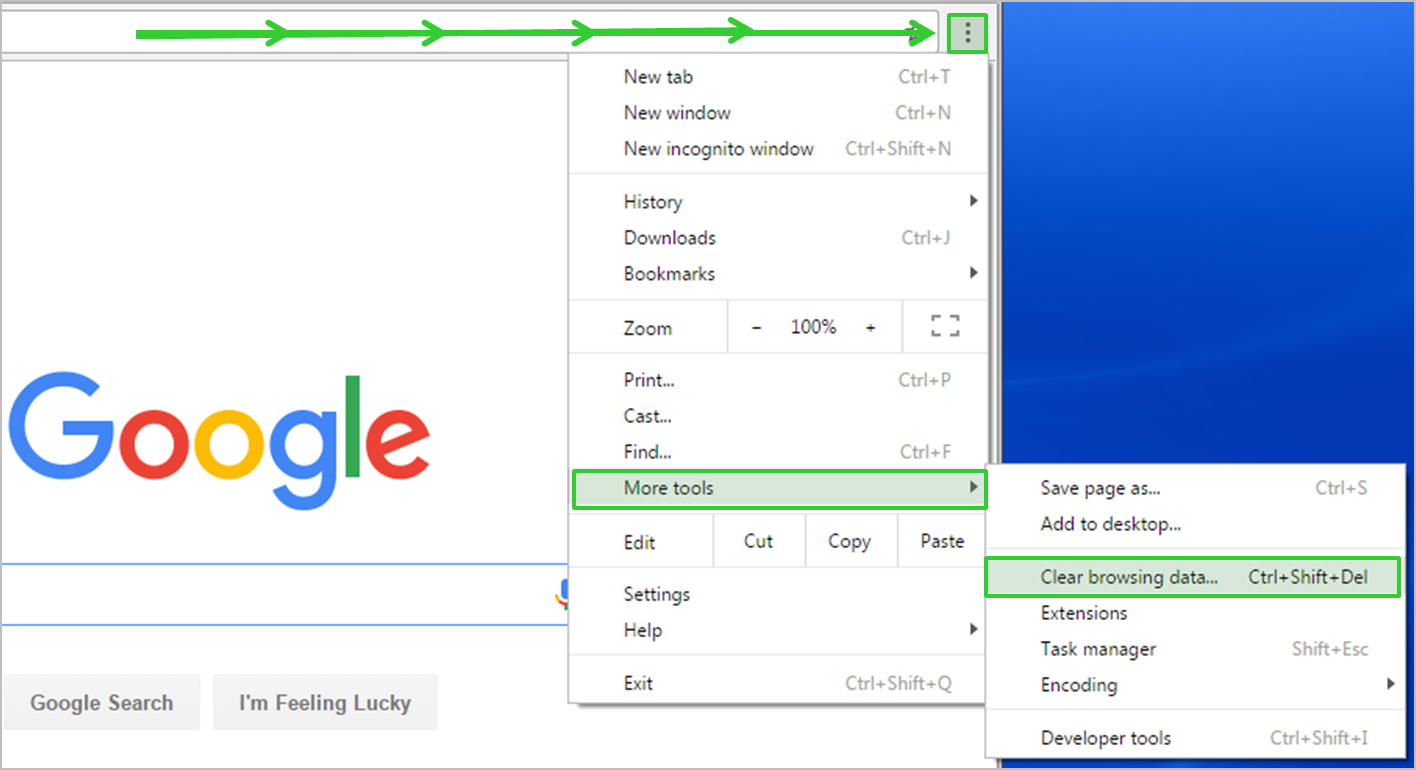
To resolve an SSL Protocol Error, one of the steps you can take is clearing your browser data and cache. This can help refresh your browser and resolve any issues related to SSL protocols. Follow these three easy steps:
1. Open your browser’s settings or options menu. This can usually be found by clicking on the three-dot menu icon in the top right corner of the browser window.
2. Look for the “Privacy” or “Security” section in the settings menu. Click on it to access the privacy and security options.
3. In the privacy or security settings, find the option to clear your browsing data or cache. Click on it to open the clearing options.
4. Select the types of data you want to clear, such as browsing history, cookies, and cached images and files. You can typically choose specific time ranges or select to clear all data.
5. After selecting the data you want to clear, click on the “Clear” or “Delete” button to initiate the process. This will remove the selected data from your browser.
6. Once the clearing process is complete, restart your browser and try accessing the website again. The SSL Protocol Error should be resolved.
Clearing your browser data and cache can help eliminate any corrupted or outdated data that might be causing the SSL Protocol Error. It’s a simple troubleshooting step that can often fix the issue and improve your browsing experience.
Checking and Updating System Date and Time
![]()
To check and update the system date and time, follow these three easy steps:
1. Open the Control Panel on your Windows computer.
2. Look for the “Date and Time” option and click on it.
3. In the Date and Time settings, make sure the date and time displayed are accurate. If not, click on the “Change date and time” button and adjust them accordingly.
Note: It is important to have the correct system date and time for various reasons, including resolving SSL protocol errors. Incorrect date and time settings can cause issues with SSL certificates and authentication processes, leading to errors when accessing secure websites or applications. By ensuring that your system’s date and time are accurate, you can help prevent SSL protocol errors and improve your overall browsing experience.
Addressing DNS Issues
1. Check your DNS settings:
– Open the Control Panel in Windows (if using Windows).
– Go to Network and Internet > Network and Sharing Center.
– Click on Change adapter settings in the left-hand menu.
– Right-click on your network connection and select Properties.
– Double-click on Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4).
– Ensure that Obtain DNS server address automatically is selected.
2. Clear your DNS cache:
– Press Windows Key + R to open the Run dialog box.
– Type cmd and press Enter to open the Command Prompt.
– Type ipconfig /flushdns and press Enter to clear the DNS cache.
3. Change your DNS server:
– Open the Control Panel in Windows (if using Windows).
– Go to Network and Internet > Network and Sharing Center.
– Click on Change adapter settings in the left-hand menu.
– Right-click on your network connection and select Properties.
– Double-click on Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4).
– Select Use the following DNS server addresses.
– Enter the preferred DNS server and alternate DNS server addresses provided by your ISP or a public DNS service like Google DNS (8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4).
Updating Browsers to the Latest Version
To update your browser to the latest version and resolve SSL Protocol Error, follow these 3 easy steps:
1. Open your browser’s settings. This can usually be done by clicking on the three-dot menu icon in the top right corner of the browser window.
2. Look for the “About” or “Help” section in the settings menu. Click on it to access information about your browser version.
3. Check for updates. Look for an option that says “Check for updates” or something similar. Click on it to start the update process. If an update is available, follow the prompts to download and install it.
Remember to restart your browser after the update to ensure the changes take effect.
Updating your browser is important as it helps ensure compatibility with the latest security protocols, including SSL. SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) is a cryptographic protocol that provides secure communication over the internet. It encrypts data transmitted between a web server and a browser, protecting it from unauthorized access.
By keeping your browser up to date, you can benefit from the latest security enhancements and features that help safeguard your online activities.
Clearing the SSL State
To clear the SSL state and resolve an SSL protocol error, follow these three easy steps:
1. Open your web browser and navigate to the settings or options menu. In Google Chrome, for example, click on the three vertical dots in the top right corner and select “Settings.”
2. Scroll down and click on “Privacy and security” or a similar option. Look for an option related to clearing browsing data or cache.
3. Click on the option to clear browsing data or cache. Make sure to select the option to clear SSL state or SSL certificates. This will remove any stored SSL certificates and resolve any SSL protocol errors you may be experiencing.
Remember to restart your browser after clearing the SSL state to ensure the changes take effect.
Adjusting Antivirus and Firewall Settings
To adjust antivirus and firewall settings to resolve an SSL protocol error, follow these three easy steps:
1. Open the Control Panel on your computer and navigate to the antivirus or firewall settings.
2. Look for an option related to SSL or HTTPS scanning. This feature may be called “SSL/TLS inspection,” “SSL/TLS scanning,” or something similar. Disable or turn off this feature.
3. Save the changes and restart your computer. Test the SSL connection again to see if the protocol error is resolved.
Disabling Unnecessary Extensions
To resolve SSL Protocol Error, you can disable unnecessary extensions in just 3 easy steps:
1. Open your browser’s settings or preferences. This can usually be found in the Control Panel for Windows users or in the browser’s menu for other operating systems.
2. Look for the “Extensions” or “Add-ons” section in the settings. Here, you will see a list of all the extensions or add-ons installed in your browser.
3. Carefully review the list and identify any extensions that are not essential for your browsing experience. These could include browser extensions that are outdated, not used frequently, or known to cause conflicts with SSL protocols.
4. Disable the unnecessary extensions by clicking on a toggle switch or an option to disable them. This will prevent the extensions from running and potentially interfering with SSL protocols.
By disabling unnecessary extensions, you can streamline your browsing experience and reduce the chances of encountering SSL Protocol Errors.
Remember, if you are unsure about a specific extension, you can always re-enable it later if needed.
Additionally, it is recommended to keep your browser and extensions up to date to ensure compatibility with the latest SSL protocols and security measures.
Modifying Internet Security and Privacy Levels
1. Update your browser and operating system: Keeping your software up to date ensures that you have the latest security patches and fixes. Visit the official website of your browser (e.
g. , Microsoft Edge) or operating system (e. g. , Windows) and download any available updates.
2. Adjust your browser settings: Open your browser and navigate to the settings or options menu. Look for the section related to security and privacy settings.
Enable or disable specific features as needed. For example, you can disable browser extensions that may interfere with SSL protocols or clear your browser cache to remove any stored data that could be causing the error. 3. Check your antivirus and firewall settings:
Antivirus software and firewalls can sometimes interfere with SSL connections. Open your antivirus program (e. g. , Microsoft Defender Antivirus) or firewall settings and look for options related to SSL or HTTPS.
Make sure these features are enabled and not blocking any necessary connections.
F.A.Qs
How to bypass ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR in Chrome?
To bypass ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR in Chrome, you can disable the QUIC protocol by typing “chrome://flags/#enable-quic” in the address bar, unchecking the QUIC protocol option, and reloading the website.
How do I unblock SSL error in Chrome?
To unblock SSL errors in Chrome, you can try the following steps:
1. Confirm that the date and time settings on your PC are correct.
2. Check the expiry date of the SSL certificate.
3. Make sure that SSL has been installed correctly.
4. Use the latest version of Google Chrome.
5. Disable SSL scanning in your antivirus software.
6. Enable the strongest 256-bit encryption instead of 128-bit.
7. Consider migrating your site from the outdated algorithm SHA-1 to SHA-2.
How to fix ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR on Microsoft edge?
To fix ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR on Microsoft Edge, you can try the following steps:
1. Verify the SSL certificate installation.
2. Fix any SSL configuration issues.
3. Update any expired SSL certificates.
4. Verify and update the system date and time.
5. Clear cookies and browser cache.
6. Check for any DNS issues.

