Is your Windows 7 64-bit system experiencing issues with Windows Update? Find out how to repair it effectively.
Preparing Your PC: Checking System Type and Disk Space
To repair Windows Update for Windows 7 64-bit systems, it is important to first check the system type and disk space on your PC.
To check the system type, follow these steps:
1. Click on the Start menu and open the Control Panel.
2. In the Control Panel, locate and click on the “System” option.
3. In the System window, you will find information about your computer, including the system type. Make sure it says “64-bit operating system” for Windows 7 64-bit systems.
Next, check the disk space on your PC by following these steps:
1. Open the File Explorer by clicking on the folder icon in the taskbar or by pressing the Windows key + E.
2. In the File Explorer, locate and click on “This PC” or “My Computer” on the left-hand side.
3. You will see a list of drives on your PC. Look for the drive where your operating system is installed, usually labeled “C:.” Right-click on this drive and select “Properties” from the context menu.
4. In the Properties window, you will see a pie chart that displays the used and free space on the drive. Make sure you have enough free space for Windows Update to function properly. As a general rule, it is recommended to have at least 10-15% of the total disk space free.
If you find that your system type is correct and you have enough disk space, you can proceed with repairing Windows Update for Windows 7 64-bit systems.
Essential Pre-Installation Steps: Backups and Antivirus Disabling
Before proceeding with the Windows Update repair process on your Windows 7 64-bit system, it is crucial to take a few essential pre-installation steps. These steps include creating backups of your important files and disabling your antivirus software temporarily.
Step 1: Back up Your Files
Creating backups of your files is crucial as it ensures that your important data is safe in case anything goes wrong during the repair process. You can use an external hard drive, USB flash drive, or any other reliable storage device to back up your files. Simply copy and paste the files you want to back up onto the external storage device.
Step 2: Disable Antivirus Software
Temporarily disabling your antivirus software is necessary to prevent any conflicts or interruptions during the repair process. Antivirus software can sometimes interfere with system updates, so it’s important to disable it before proceeding.
To disable your antivirus software, follow these steps:
1. Locate the antivirus software icon in your system tray, typically found in the bottom-right corner of your screen.
2. Right-click on the antivirus software icon to open a context menu.
3. Look for an option like “Disable” or “Turn Off” and click on it.
4. Confirm the action if prompted.
Remember to re-enable your antivirus software after completing the Windows Update repair process to ensure ongoing protection for your system.
Utilizing Windows Update and Microsoft Update Catalog for SP1 Installation
To repair Windows Update for Windows 7 64-bit systems, you can utilize Windows Update and the Microsoft Update Catalog to install Service Pack 1 (SP1). Follow these steps:
1. Open the Start menu and search for “Windows Update.”
2. Click on “Windows Update” from the search results to open the Windows Update control panel.
3. Click on “Check for updates” to search for available updates.
4. Once the search is complete, locate and select “Service Pack 1 for Microsoft Windows (KB976932)” from the list of updates.
5. Click on the “Install” button to start the installation process.
6. Follow the on-screen prompts to complete the installation of SP1.
7. If prompted, restart your computer to apply the changes.
Alternatively, you can also download the SP1 installation package from the Microsoft Update Catalog. Here’s how:
1. Visit the Microsoft Update Catalog website (catalog.update.microsoft.com) in your web browser.
2. In the search box, type “Service Pack 1 for Windows 7 64-bit” and press Enter.
3. Locate the correct version of SP1 for your system (based on the architecture – x86 or x64) and click on the “Download” button next to it.
4. Save the downloaded file to a location on your computer, such as the desktop.
5. Once the download is complete, double-click on the downloaded file to start the installation.
6. Follow the on-screen prompts to complete the installation of SP1.
7. Restart your computer if prompted.
By utilizing Windows Update and the Microsoft Update Catalog, you can easily repair Windows Update on your Windows 7 64-bit system by installing Service Pack 1.
Running the Windows Update Troubleshooter for Common Errors
To troubleshoot common errors with Windows Update on a Windows 7 64-bit system, you can use the Windows Update Troubleshooter. This tool can help identify and fix issues that may be preventing Windows Update from working correctly.
Here’s how to run the Windows Update Troubleshooter:
1. Open the Control Panel on your computer. You can do this by clicking the Start button and selecting Control Panel from the menu.
2. In the Control Panel, search for “Troubleshooting” in the search bar at the top-right corner of the window.
3. Click on the “Troubleshooting” option that appears in the search results.
4. In the Troubleshooting window, click on “Fix problems with Windows Update” under the System and Security section.
5. The Windows Update Troubleshooter will open. Click on the “Next” button to start the troubleshooting process.
6. The tool will scan your system for any issues related to Windows Update. If it finds any problems, it will provide you with options to fix them.
7. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the troubleshooting process.
8. Once the troubleshooting is complete, restart your computer.
By running the Windows Update Troubleshooter, you can resolve common errors that may be preventing Windows Update from functioning properly on your Windows 7 64-bit system. This tool can help ensure that your computer stays up to date with the latest security patches and software updates from Microsoft.
Repairing System Corruption: Using DISM and CheckSUR
To repair system corruption and fix Windows Update issues on Windows 7 64-bit systems, you can use DISM (Deployment Image Servicing and Management) and CheckSUR (System Update Readiness Tool). These tools are designed to scan and repair corrupted system files that may be causing problems with Windows Update.
To start, open an elevated Command Prompt by pressing the Windows key + X and selecting “Command Prompt (Admin).” Alternatively, you can search for “cmd” in the Start menu, right-click on “Command Prompt,” and choose “Run as administrator.”
DISM is a command-line tool that can be used to scan and repair the Windows system image. To use DISM, run the following command:
dism /online /cleanup-image /restorehealth
This command will scan your system for corruption and attempt to repair any issues it finds. It may take some time to complete, so be patient.
Once DISM finishes its scan and repair process, you can use the CheckSUR tool to further diagnose and fix Windows Update problems. CheckSUR is a standalone tool provided by Microsoft to address specific issues related to Windows Update.
Download the appropriate version of CheckSUR for your operating system from the Microsoft website. Make sure to choose the version that matches your system architecture (64-bit in this case).
Once downloaded, run the CheckSUR tool by double-clicking on the downloaded file. The tool will automatically scan your system for inconsistencies and attempt to fix them. Again, this process may take some time, so be patient.
After both DISM and CheckSUR have completed their scans and repairs, restart your computer and try updating Windows again. Hopefully, these steps will resolve any system corruption issues and allow Windows Update to function properly.
Verifying System Integrity and Analyzing Logs
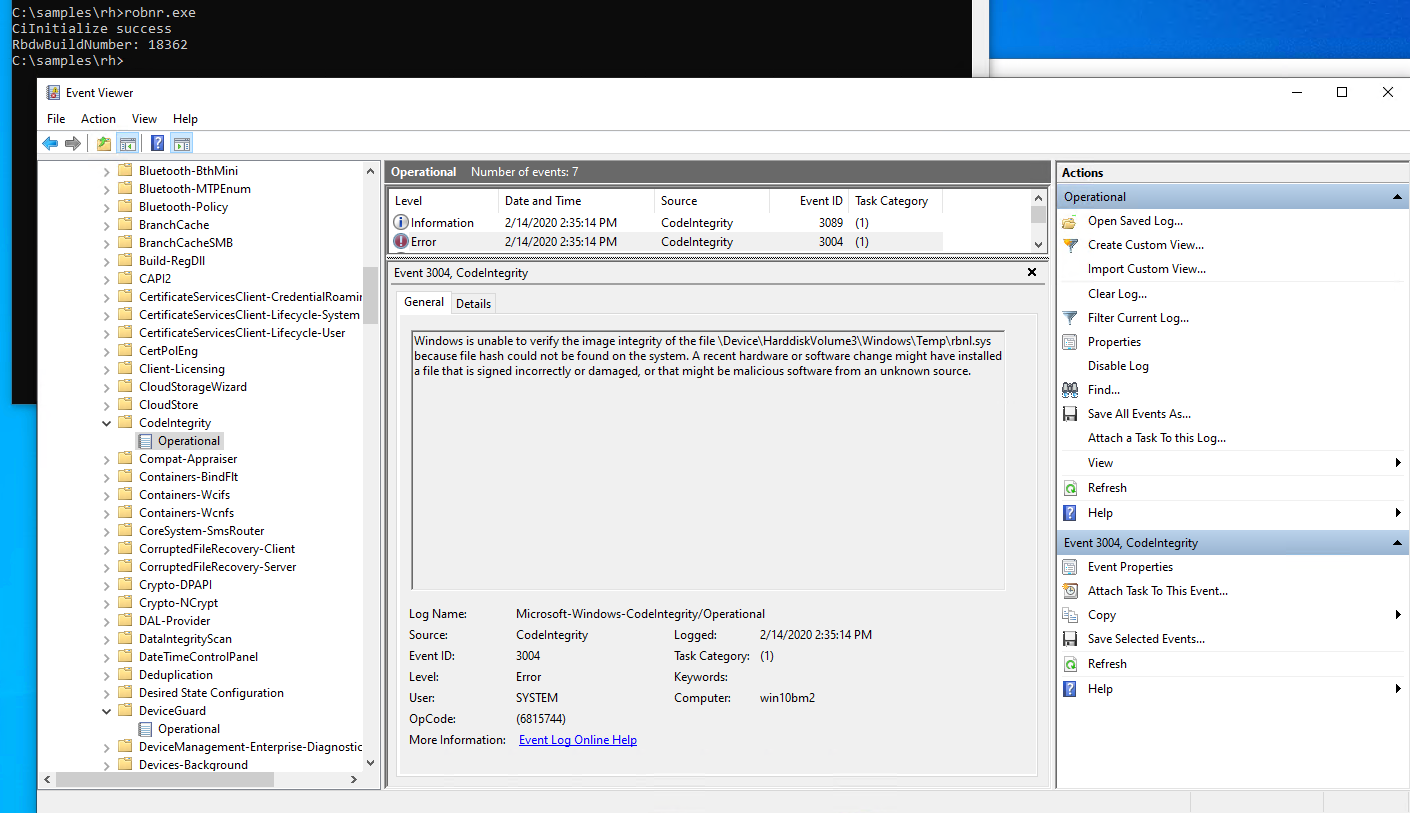
To verify system integrity and analyze logs for Windows 7 64-bit systems, follow these steps:
1. Run the System File Checker tool: Open a command prompt with administrative privileges by pressing the Windows key + X and selecting “Command Prompt (Admin).” In the command prompt window, type “sfc /scannow” and press Enter. This will scan and repair any corrupt or missing system files.
2. Check the Windows Update logs: Open the Event Viewer by pressing the Windows key + R, typing “eventvwr.msc” in the Run dialog box, and pressing Enter. Navigate to “Windows Logs” > “System” and look for any errors or warnings related to Windows Update. This can help identify the cause of update failures.
3. Analyze the CBS log: The Component-Based Servicing (CBS) log provides detailed information about the installation of Windows updates. Open a command prompt with administrative privileges and type “findstr /c:”[SR]” %windir%\Logs\CBS\CBS.log >”%userprofile%\Desktop\sfcdetails.txt”” to extract the relevant information and save it to a text file on your desktop. Open the generated “sfcdetails.txt” file to review the contents.
4. Use the System Update Readiness Tool: Download and install the Windows Update Readiness Tool from the Microsoft website. This tool scans for inconsistencies in the Windows servicing store and can help resolve update-related issues.
5. Clear the Windows Update cache: Open a command prompt with administrative privileges and type “net stop wuauserv” to stop the Windows Update service. Then, navigate to the “%windir%\SoftwareDistribution” folder and delete its contents. Restart the Windows Update service by typing “net start wuauserv” in the command prompt.
Data Collection Practices for Troubleshooting
- Run Windows Update Troubleshooter:
- Press the Windows key on your keyboard and type “troubleshoot”.
- Select Troubleshoot from the search results.
- In the Troubleshoot window, click on Windows Update and then click Run the troubleshooter.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the troubleshooting process.
- Check for Windows Update errors:
- Press the Windows key on your keyboard and type “troubleshoot”.
- Select Troubleshoot from the search results.
- In the Troubleshoot window, click on Windows Update and then click Advanced.
- Check the Apply repairs automatically box and click Next.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to check for and fix any Windows Update errors.
- Reset Windows Update components:
- Press the Windows key on your keyboard and type “cmd”.
- Right-click on Command Prompt and select Run as administrator.
- In the Command Prompt window, type the following commands one by one and press Enter after each command:
- net stop wuauserv
- net stop cryptSvc
- net stop bits
- net stop msiserver
- After running the above commands, type the following commands one by one and press Enter after each command:
- ren C:\Windows\SoftwareDistribution SoftwareDistribution.old
- ren C:\Windows\System32\catroot2 catroot2.old
- Finally, type net start wuauserv and press Enter.
- Perform a clean boot:
- Press the Windows key on your keyboard and type “msconfig”.
- Select System Configuration from the search results.
- In the System Configuration window, click on the Services tab.
- Check the Hide all Microsoft services box and click Disable all.
- Click on the Startup tab and click Open Task Manager.
- In the Task Manager window, disable all startup items by right-clicking on each item and selecting Disable.
- Close the Task Manager and go back to the System Configuration window. Click OK and then click Restart.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I fix Windows 7 unable to update?
To fix Windows 7 unable to update, you can try the following steps:
1. Stop the Automatic Updates service.
2. Rename the software distribution folder (e.g., C:\Windows\SoftwareDistribution).
3. Restart the Automatic Update service.
4. Open CMD and run wuauclt /resetauthorization /detectnow.
5. Open CMD and run wuauclt /reportnow.
Are old Windows 7 updates still available?
No, old Windows 7 updates are no longer available since support for Windows 7 has ended.
How do I restart Windows Update service in Windows 7?
To restart Windows Update service in Windows 7, follow these steps:
1. Press the Windows logo Key+R to open the Run box.
2. Type services.msc in the Run box and press Enter.
3. Right-click Windows Update in the Services management console and select Stop.
4. After Windows Update stops, right-click Windows Update and select Start.

