In this article, I will discuss the steps to fix corrupt registry issues in Windows Vista.
Understanding Windows Registry and Common Errors
![]()
The Windows Registry is a hierarchical database that stores important settings and configurations for the Windows operating system. However, it can sometimes become corrupt, leading to various errors and issues on your computer. In this article, we will provide you with some tips on fixing a corrupt registry in Windows Vista.
One common method for fixing registry errors is to use a registry cleaner tool. These tools can scan your registry for errors, invalid entries, and other issues, and then fix them automatically. CCleaner is a popular registry cleaner that you can use for this purpose.
Another option is to use the System Restore feature in Windows Vista. System Restore allows you to revert your system back to a previous state, including the registry. This can help fix any issues that were caused by recent changes to the registry.
If you are experiencing serious issues with your computer, you may need to use the Recovery Console. The Recovery Console is a command-line interface that allows you to access and repair your computer’s operating system. You can use the Recovery Console to manually restore a backup of the registry or run the System File Checker tool to fix any corrupted system files.
It’s also a good practice to regularly back up your registry. This will allow you to restore a working version of the registry if anything goes wrong. You can use the Windows Vista backup utility or a third-party backup tool to create a backup of your registry.
Identifying Signs and Causes of Registry Problems
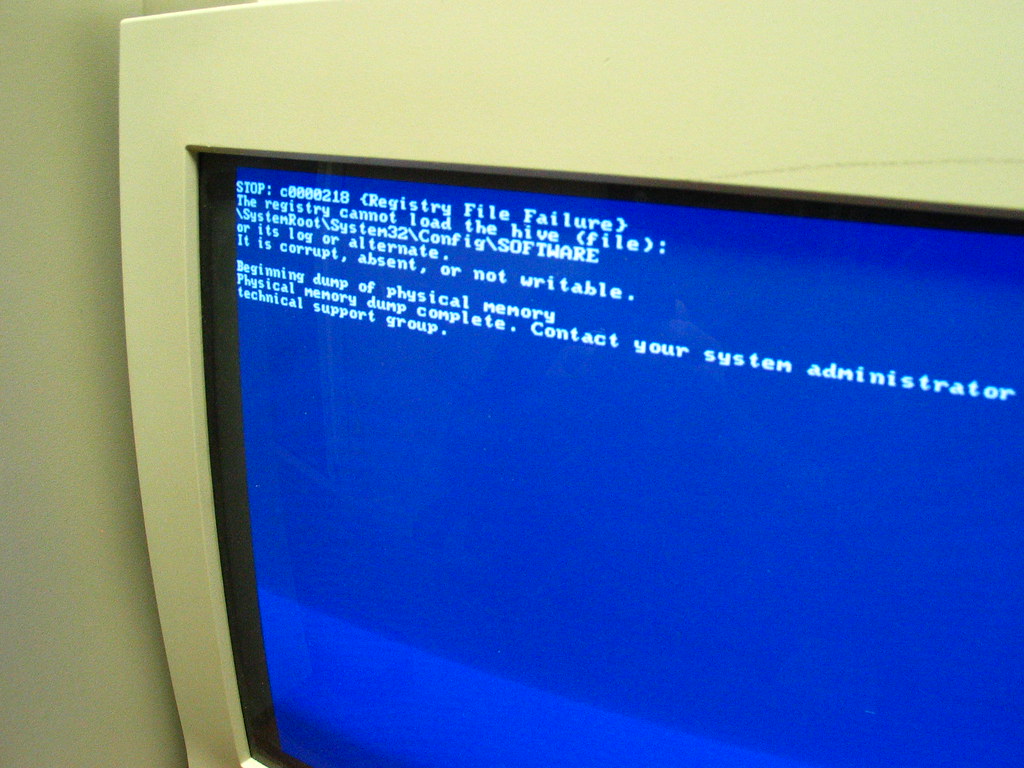
- Slow computer performance
- Programs taking longer to open or run
- Frequent freezes or crashes
- Error messages
- Blue screen errors
- Application-specific errors
- Unexpected system behavior
- Programs not responding
- Missing or corrupted files
- Identify potential causes
- Recent software installations or updates
- Malware or virus infections
- Incomplete or unsuccessful software uninstallations
- Perform a system scan
- Launch Windows Defender or any reliable anti-virus software
- Perform a full system scan to detect and remove any malware or viruses
- Check for recent software installations or updates
- Open Control Panel
- Click on Programs or Programs and Features
- Review the list of installed programs or updates
- Identify any recent installations or updates that may have caused the registry problems
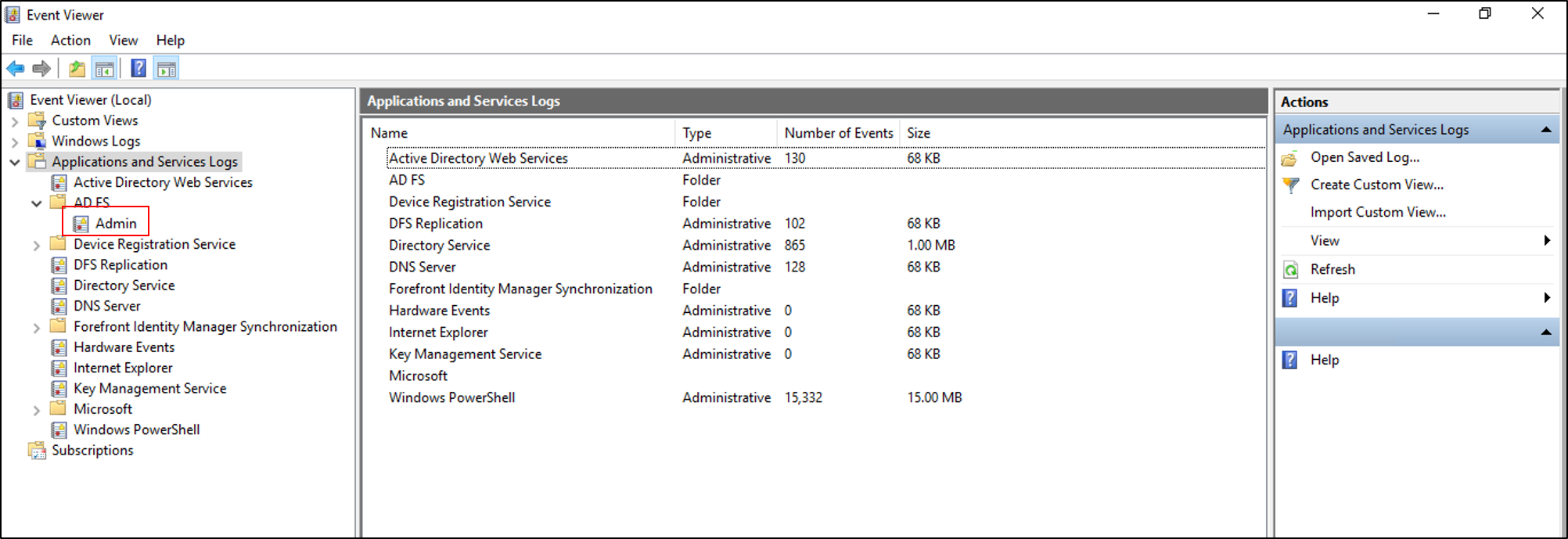
- Review system logs
- Open Event Viewer by pressing Win+R and typing “eventvwr.msc“
- Navigate to Windows Logs and then Application
- Look for any error or warning messages related to registry issues
- Note down the Event ID and Source for further investigation
- Use System Restore
- Open System Restore by pressing Win+R and typing “rstrui.exe“
- Select a restore point prior to the occurrence of registry problems
- Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the restoration process
- Consult professional help
- If the above steps do not resolve the registry problems, it is recommended to seek assistance from a professional technician or IT support
Strategies for Fixing Registry Issues
1. Use System Restore: If you recently made changes to your computer that resulted in registry issues, you can use System Restore to revert your system back to a previous state. This can help fix corrupt registry entries.
2. Run the System File Checker: The System File Checker is a built-in Windows tool that scans for and restores corrupted system files, including registry files. To run it, open the Command Prompt as an administrator and type sfc /scannow.
3. Use a Registry Cleaner: There are various third-party registry cleaner tools available, such as CCleaner, that can help fix corrupt registry entries. These tools scan your registry for errors and provide an option to fix them.
4. Manually Edit the Registry: This option should only be used by advanced users who are confident in their knowledge of the Windows registry. To manually edit the registry, open the Registry Editor by typing regedit in the Run dialog box. From there, you can navigate to the specific registry key causing the issue and make the necessary changes.
5. Reinstall Windows: If all else fails and the registry issues persist, you may need to consider reinstalling Windows Vista. This will restore your system to its original state and fix any corrupt registry entries. Make sure to back up your important files before proceeding with a reinstall.
Essential Tools for Registry Repair and Cleanup
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| Registry Cleaner | A registry cleaner is a software tool that scans your Windows Vista registry for corrupt, invalid, or obsolete entries and helps remove them. It helps optimize the registry by fixing errors and improving system performance. |
| Registry Editor | The Registry Editor is a built-in Windows tool that allows you to view, modify, and manage the registry. It is a powerful tool that should be used with caution, as incorrect changes to the registry can cause system instability. |
| System Restore | System Restore is a Windows feature that allows you to revert your system back to a previous state. It can be used to undo changes made to the registry if they caused issues. System Restore creates restore points that you can use to roll back your system. |
| Backup and Restore Center | The Backup and Restore Center is a Windows Vista tool that allows you to create backups of your system, including the registry. It is recommended to regularly backup your registry before making any changes to ensure you can restore it if needed. |
| Command Prompt | The Command Prompt is a command-line tool in Windows Vista that allows you to execute commands and perform various tasks. It can be used to run registry-related commands, such as exporting, importing, or repairing the registry. |
Importance of Backing Up the Registry
Backing up the registry is crucial when attempting to fix a corrupt registry in Windows Vista. It ensures that you have a backup of your registry settings before making any changes, protecting you from potential data loss or system instability. By creating a backup, you can easily restore your registry to its previous state if something goes wrong during the fixing process.
To back up the registry in Windows Vista, follow these steps:
1. Click on the Start menu and type “regedit” in the search bar. Press Enter to open the Registry Editor.
2. In the Registry Editor, click on the “File” menu at the top left corner and select “Export”. This will open the Export Registry File window.
3. Choose a location to save the backup file, such as a USB drive or an external hard disk. Give the backup file a descriptive name that you can easily recognize later.
4. In the Export Range section, select “All” to back up the entire registry. Alternatively, you can select specific branches if you only want to back up certain parts of the registry.
5. Click on the “Save” button to create the backup. Wait for the process to complete, which may take a few seconds to a few minutes depending on the size of your registry.
Once the backup is created, you can proceed with fixing the corrupt registry. Remember to always be cautious when making changes to the registry, as incorrect modifications can lead to serious issues. Having a backup ensures that you can easily revert back to a working state if necessary.
Advanced Techniques: Editing and Cleaning the Registry
Editing and cleaning the registry is a crucial step in fixing a corrupt registry in Windows Vista. To perform these advanced techniques effectively, follow the instructions below:
1. Backup the Registry: Before making any changes to the registry, it’s essential to create a backup. This ensures that you can restore the registry if any issues arise. To create a backup:
a. Press the Windows key + R to open the Run dialog box.
b. Type “regedit” and press Enter to open the Registry Editor.
c. In the Registry Editor, click on “File” in the top menu.
d. Select “Export” to create a backup of the entire registry or choose a specific branch to export.
2. Editing the Registry: To edit the registry, follow these steps:
a. Open the Registry Editor by pressing the Windows key + R and typing “regedit.”
b. Navigate to the specific registry key you want to edit using the folder tree on the left-hand side.
c. Right-click on the key and select “Modify.”
d. Enter the new value or modify the existing value in the “Value data” field.
e. Click “OK” to save the changes.
3. Cleaning the Registry: Cleaning the registry involves removing unnecessary or invalid entries. Follow these steps:
a. Use a reliable registry cleaner software such as CCleaner or Wise Registry Cleaner.
b. Download and install the software, then open it.
c. Select the “Registry Cleaner” option.
d. Click on the “Scan for Issues” button to identify registry problems.
e. Once the scan is complete, click on the “Fix selected issues” button to clean the registry.
F.A.Qs
How do I fix a corrupted registry?
To fix a corrupted registry, you can try the following steps:
– Run the Disk Cleanup Tool.
– Use Automatic Startup Repair.
– Run the System File Checker.
– Run the DISM Scan.
– Import a Registry Backup.
– Run CCleaner Registry Cleaner.
– Scan Your System for Malware.
– Use a System Restore Point.
What causes corrupt registry files?
Corrupt registry files can be caused by damage or changes to the computer’s local disk, such as power failures during system updates that result in incomplete changes to the registry.
Does Windows have a registry repair tool?
Windows does have a registry repair tool called Windows Registry Checker.
How do I remove bad registry entries?
To remove bad registry entries, you can follow these steps:
Start Registry Editor (Regedit.exe).
Locate the specific key that needs to be deleted by finding the key name created by the program.
To create a backup, go to the Registry menu and export the selected registry key.
Delete the selected registry key and its values.
Exit Registry Editor.

