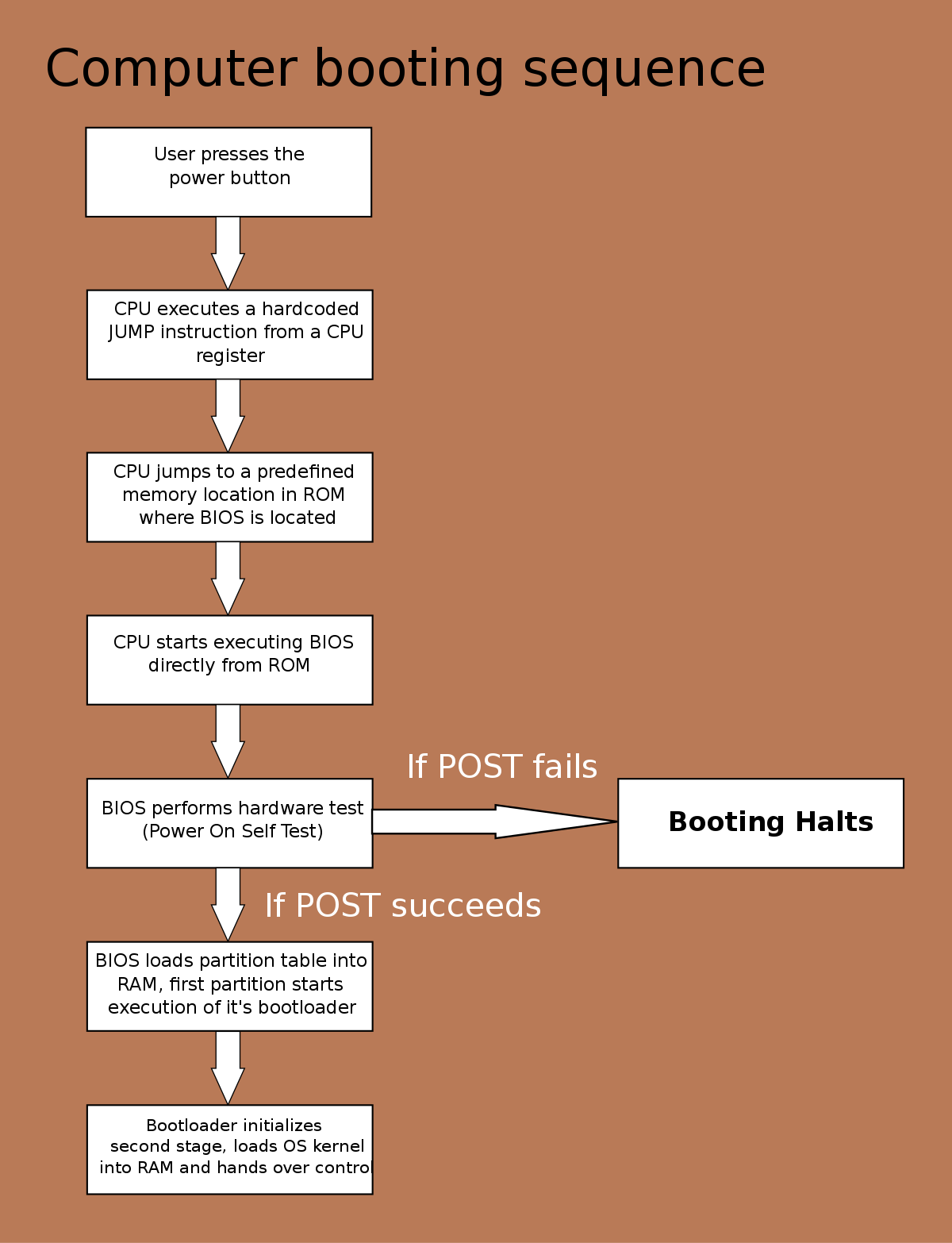
Having a random blue screen on your PC can be frustrating and disruptive. In this article, we will explore effective solutions to fix this issue and ensure smooth operation.
Understanding and Preventing System Crashes
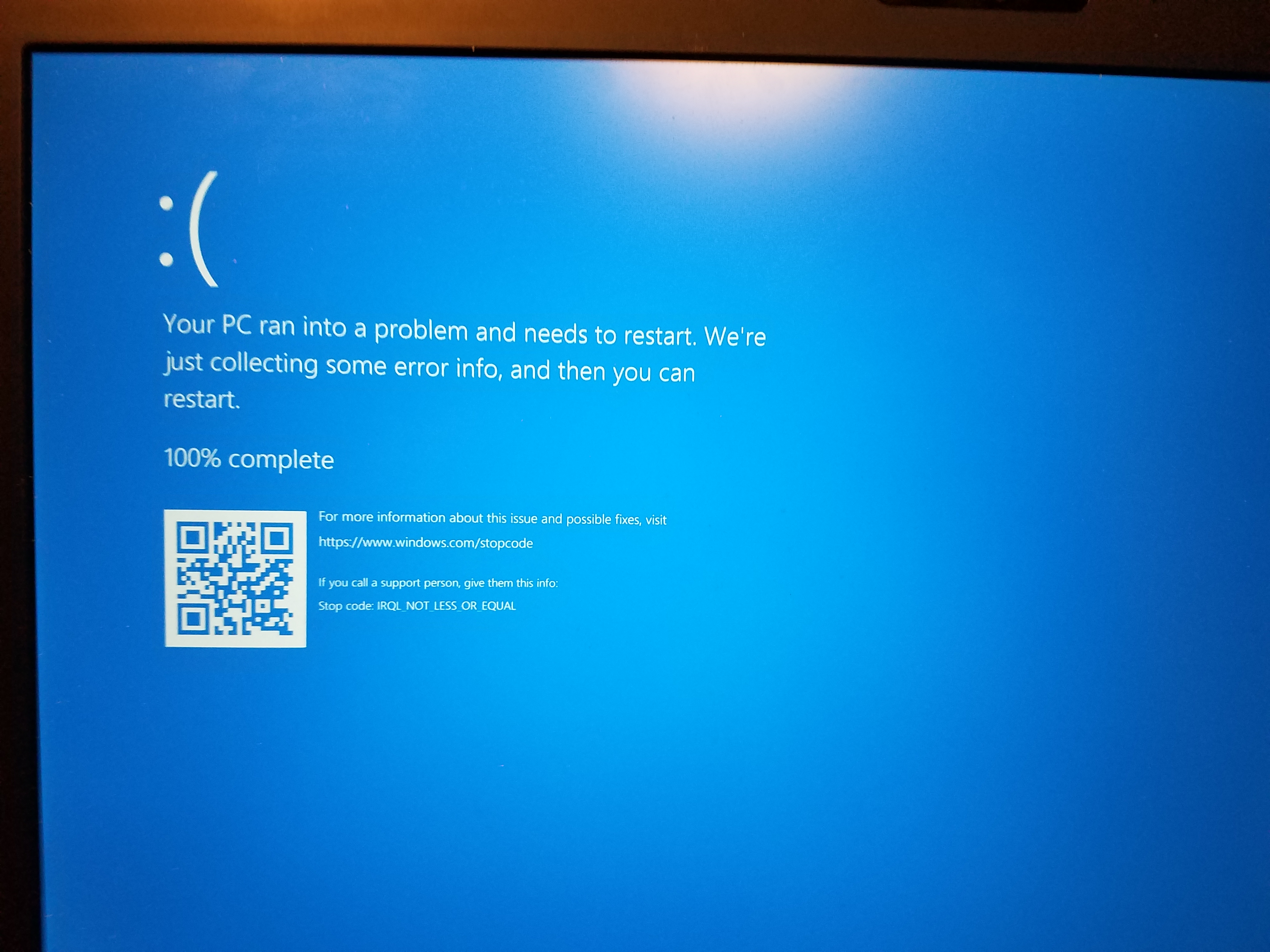
System crashes can be frustrating and disruptive, but with the right knowledge and preventive measures, you can avoid them and keep your PC running smoothly. Here are some tips to help you understand and prevent system crashes:
1. Update your software and drivers regularly. Keeping your operating system, drivers, and software up to date is crucial in preventing system crashes. Outdated software and drivers can contain bugs or compatibility issues that may lead to crashes. Check for updates regularly and install them promptly.
2. Scan for malware and spyware. Malware and spyware can cause system crashes and other issues. Use a reliable antivirus program to scan your PC for any malicious software. Also, make sure to keep your antivirus software updated to ensure it can detect and remove the latest threats.
3. Check your hardware. Faulty hardware can also cause system crashes. Check your computer’s hardware components, such as the motherboard, graphics card, and RAM, for any signs of damage or malfunction. If you suspect a hardware issue, consider consulting a professional or replacing the faulty component.
4. Keep your system cool. Overheating can cause system crashes. Make sure your computer is in a well-ventilated area and that its cooling system, such as fans or liquid cooling, is functioning properly. Regularly clean out any dust or debris that may accumulate inside your computer case.
5. Run a disk check. Corrupted or damaged files can lead to system crashes. Use the CHKDSK command to scan your computer’s hard drive for errors and fix them. This can help prevent crashes caused by file corruption.
6. Use safe mode for troubleshooting. If you’re experiencing frequent crashes, booting your computer in safe mode can help identify the cause. Safe mode starts your computer with only the essential drivers and services, making it easier to pinpoint any software or driver issues. To enter safe mode, restart your computer and repeatedly press the F8 key before the Windows logo appears.
7. Monitor your system’s resources. Excessive resource usage can cause crashes. Use the Task Manager to keep an eye on your computer’s CPU, memory, and disk usage. If any program or process is using an unusually high amount of resources, it may be causing crashes. Consider closing or uninstalling the problematic software.
8. Keep backups of important data. In case of a system crash, having backups of your important files is essential. Regularly back up your data to an external hard drive, USB flash drive, or cloud storage. This way, even if your system crashes, you can still retrieve your important files.
9. Avoid overclocking. Overclocking your CPU or GPU can increase the risk of system crashes. While it may provide a performance boost, overclocking puts additional stress on your hardware, which can lead to instability and crashes. Stick to the manufacturer’s recommended specifications to ensure stability.
10. Consult professional help if needed. If you’re unable to fix or identify the cause of system crashes, consider seeking professional assistance. IT professionals can diagnose and resolve complex issues that may be causing crashes. Don’t hesitate to reach out for help if you’re unsure about how to proceed.
Steps for Troubleshooting and Repairs
-
Check for Hardware Issues:
- Inspect the computer’s hardware components for any physical damage or loose connections.
- Ensure that all cables and peripherals are properly connected.
- If possible, test the computer with different hardware components to identify if a specific device is causing the issue.
-
Update Device Drivers:
- Open Device Manager by pressing Windows key + X and selecting it from the menu.
- Expand the different categories and look for any devices with a yellow exclamation mark, indicating a driver issue.
- Right-click on the problematic device and select Update driver.
- Choose to search automatically for updated driver software, and let the process complete.
- Repeat this process for all devices with driver issues.
-
Scan for Malware:
- Install and run a reputable antivirus or anti-malware software.
- Perform a full system scan to detect and remove any malicious software.
- Ensure that the antivirus software is up to date.
-
Check for System Updates:
- Open Windows Update by pressing Windows key + I and selecting Update & Security.
- Click on Check for updates and install any available updates.
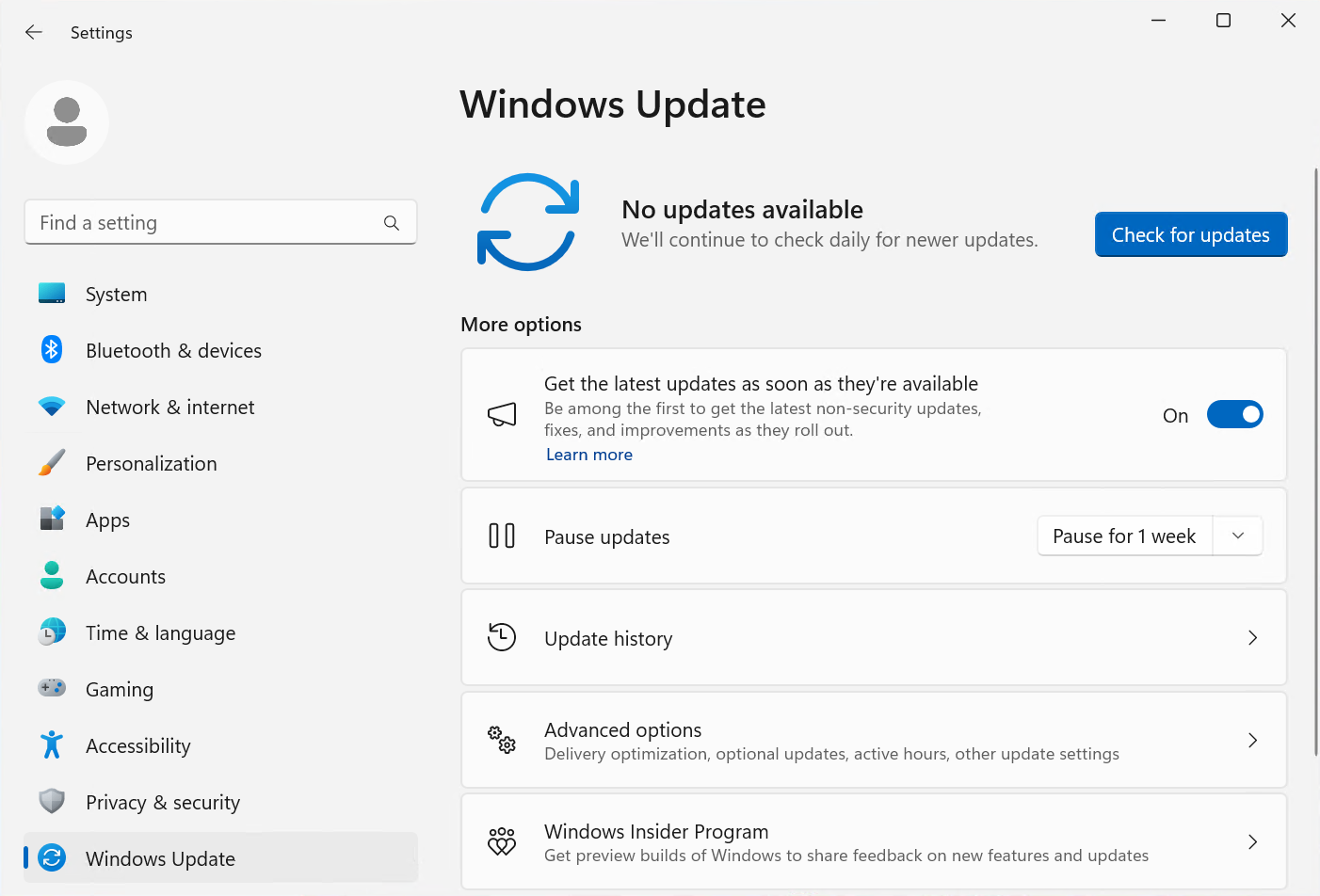
- Restart the computer after the updates are installed.
-
Run System File Checker (SFC) and DISM:
- Open Command Prompt as an administrator by pressing Windows key + X and selecting Command Prompt (Admin).
- Type sfc /scannow and press Enter to run the System File Checker.
- Wait for the scan to complete and follow any instructions provided.
- Once done, type dism /online /cleanup-image /restorehealth and press Enter to run the Deployment Image Servicing and Management (DISM) tool.
- Let the process finish, then restart the computer.
-
Check for Overheating:
- Ensure that the computer’s cooling system is functioning properly.
- Clean any dust or debris from the fans and vents.
- Consider using a cooling pad or additional cooling solutions.
- Monitor the computer’s temperature using appropriate software and take necessary actions if it exceeds safe limits.
-
Perform a System Restore:
- Open System Restore by pressing Windows key + R, typing rstrui.exe, and pressing Enter.
- Select a restore point from a time when the computer was not experiencing blue screen errors.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to initiate the system restore process.
- Let the process complete, and the computer will restart.
-
Reinstall Windows:
- Ensure that you have a backup of your important files.
- Insert the Windows installation media (USB or DVD) into the computer.
- Restart the computer and boot from the installation media.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to reinstall Windows, formatting the system drive if necessary.
- After the installation, reinstall necessary drivers and software.
- Restore your backed-up files to the computer.
DIY Repair Cautions and Solutions

1. Identify the error message: When you encounter a blue screen error on your PC, it’s important to pay attention to the error message displayed. This message can provide valuable clues about the underlying issue.
2. Check for software conflicts: Random blue screens can often be caused by software conflicts or bugs. Before diving into hardware troubleshooting, try updating or uninstalling any recently installed software that may be causing the issue.
3. Update device drivers: Outdated or incompatible device drivers can also lead to blue screen errors. Use the Device Manager to check for any outdated drivers and update them accordingly. Right-click on the Start button, select Device Manager, and look for any devices with a yellow exclamation mark. Right-click on the device and choose Update Driver.
4. Run a memory diagnostic test: Random blue screens can sometimes be caused by faulty RAM. Windows 10 has a built-in memory diagnostic tool that can help identify and fix any memory-related issues. Open the Start menu, type “Windows Memory Diagnostic” and select the corresponding result. Follow the on-screen instructions to run the test.
5. Check for hard drive errors: Corrupted or failing hard drives can also lead to blue screen errors. Use the CHKDSK tool to scan and repair any errors on your hard drive. Open Command Prompt as an administrator, type “chkdsk /f” followed by the drive letter of the affected drive (e.g., C:), and press Enter. Follow the prompts to schedule a disk check and restart your PC.
6. Update BIOS: Outdated BIOS firmware can cause compatibility issues and lead to blue screen errors. Visit your motherboard manufacturer’s website and download the latest BIOS update. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to update your BIOS.
7. Check for overheating: Overheating can cause system instability and random blue screens. Ensure that your PC’s cooling system is functioning properly, clean any dust from the fans, and consider using a cooling pad or additional case fans if necessary.
8. Scan for malware: Malicious software can also cause random blue screens. Run a full system scan using a reliable antivirus program to check for any malware infections.
9. Remove recently added hardware: If you recently installed new hardware, such as a graphics card or RAM, remove it and see if the blue screens persist. Faulty or incompatible hardware can cause system crashes.
10. Reset Windows: If all else fails, you can try resetting your Windows installation. This will reinstall the operating system while keeping your personal files intact. Open the Settings app, go to Update & Security, select Recovery, and click on the “Get started” button under Reset this PC. Follow the prompts to reset your PC.
The Bottom Line on System Stability
1. Check for hardware issues: Ensure that all your computer hardware components, such as RAM, hard drives, and graphics cards, are properly connected and functioning correctly. Use the Device Manager or third-party software to check for any faulty hardware.
2. Update device drivers: Outdated or incompatible device drivers can cause system instability. Visit the manufacturer’s website or use third-party software to update your drivers. Make sure to uninstall the old drivers before installing the new ones.
3. Remove any recently installed software or updates: If you recently installed new software or updates, try uninstalling them to see if it resolves the blue screen issue. Use the Control Panel or third-party software for easy removal.
4. Scan for malware and viruses: Malware and viruses can cause system instability and lead to blue screens. Use reliable antivirus software to scan your PC and remove any threats.
5. Check for software conflicts: Some software programs can conflict with each other and cause system crashes. Disable or uninstall any recently installed software that might be causing conflicts.
6. Verify system files: Corrupt system files can also lead to blue screens. Open the Command Prompt as an administrator and run the “sfc /scannow” command to scan and repair any corrupt system files.
7. Update your operating system: Keeping your operating system up to date is essential for system stability. Install the latest updates and patches provided by Microsoft for your version of Windows.
8. Monitor system temperature: Overheating can cause random blue screens. Monitor your system’s temperature using third-party software and ensure that all fans are working properly. Clean any dust buildup inside your computer to improve airflow.
9. Test your RAM: Faulty RAM modules can cause system crashes. Run a memory diagnostic tool, such as Windows Memory Diagnostic or MemTest86, to check for any issues.
10. Perform a clean boot: A clean boot allows you to start your PC with a minimal set of drivers and startup programs. This can help identify if any third-party software is causing the blue screens. Follow the instructions provided by Microsoft to perform a clean boot.
F.A.Qs
Why does my PC keep blue screening while gaming?
Your PC may keep blue screening while gaming due to the graphic-intensive nature of the games. This can push your hardware to its limits, potentially revealing underlying weaknesses, overheating issues, or software conflicts.
Why does my screen turn blue sometimes?
Sometimes screens turn blue due to a variety of reasons such as improperly installed hardware, damaged hardware, aging hardware, buggy or incompatible software, or driver updates that fail to integrate properly with the system.
Is blue screen of death fixable?
The blue screen of death (BSOD) is fixable. When Windows reboots after a BSOD, it automatically troubleshoots and begins the repair process.

