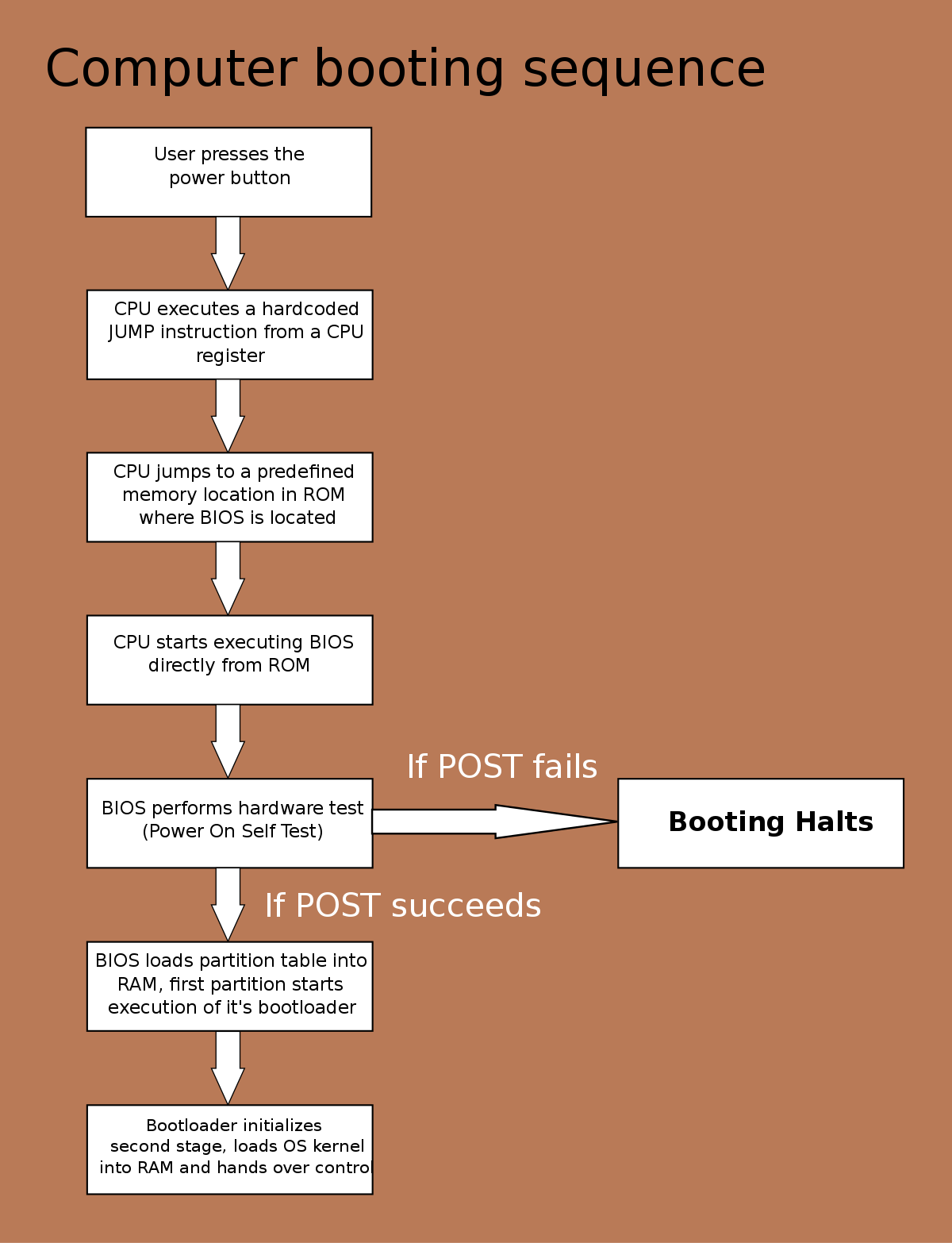
Having trouble fixing a failed system recovery on Windows 7? Look no further for a solution.
Description and Symptoms
When attempting to perform a system recovery on Windows 7, it can sometimes fail. This can be a frustrating issue, but there are steps you can take to fix it.
One common symptom of a failed system recovery is an error message that appears during the process. This error message may indicate that the recovery was unsuccessful and provide some details about the issue.
Another symptom is that the system may not boot properly after the recovery attempt. You may see a black screen, a blue screen with an error message, or the system may continuously restart.
In some cases, you may also notice that certain programs or files are missing or inaccessible after the failed recovery.
To fix a failed system recovery on Windows 7, there are a few troubleshooting steps you can try.
First, try booting the computer into Safe Mode. This can help isolate any software conflicts that may be causing the issue. To do this, restart the computer and repeatedly press the F8 key until the Advanced Boot Options menu appears. Use the arrow keys to select Safe Mode and press Enter.
If Safe Mode does not work, you can try using the Windows 7 installation disc or a boot disk. Insert the disc or boot disk and restart the computer. Follow the on-screen instructions to access the System Recovery Options. From there, you can attempt to repair the system using the Startup Repair tool or restore from a system image backup.
You can also try using the Command Prompt. Open the Command Prompt from the System Recovery Options menu and use commands such as sfc /scannow or chkdsk /f to scan and repair system files or check and repair disk errors.
If none of these methods work, you may need to consider other options such as reinstalling Windows 7 or seeking technical support.
It’s always a good idea to have a backup of your important files and data before attempting any system recovery. This way, you can restore your files if anything goes wrong during the process.
Common Causes and Symptoms
When attempting to perform a system recovery on Windows 7, it is not uncommon to encounter issues that can prevent the process from being successful. Understanding the common causes and symptoms of these failures can help you troubleshoot and resolve the issue quickly.
One common cause of system recovery failure is a corrupted Windows Registry. The Windows Registry is a crucial component of the operating system that stores important settings and configurations. If the registry becomes corrupted, it can disrupt the system recovery process. To fix this issue, you can use the Windows Registry Editor to manually repair any corrupt entries.
Another potential cause of system recovery failure is interference from antivirus software. Some antivirus programs may mistakenly identify the system recovery process as a threat and block it from completing. To resolve this, you can temporarily disable your antivirus software before attempting the system recovery.
Issues with booting can also contribute to system recovery failures. If your computer is unable to boot properly, the system recovery process may not be able to complete successfully. To troubleshoot booting issues, you can try using the Windows Preinstallation Environment (WinPE) to access advanced recovery options.
Disk partitioning problems can also hinder system recovery. If the disk partitions on your computer are not properly configured, the system recovery may fail. You can use a disk partitioning tool, such as Disk Management or a third-party software, to check and adjust the disk partitions if necessary.
It is important to note that system recovery failures can manifest in various symptoms. Some common symptoms include error messages during the recovery process, the system getting stuck or freezing during recovery, or the system restarting without completing the recovery. These symptoms can indicate the specific cause of the failure and guide your troubleshooting efforts.
Disable Interfering Antivirus Software
1. Open the Start menu and type “msconfig” in the search bar. Press Enter to open the System Configuration utility.
2. In the System Configuration window, navigate to the “Services” tab.
3. Check the box next to “Hide all Microsoft services” to prevent accidentally disabling essential system services.
4. Scroll through the list of services and locate your antivirus software. Uncheck the box next to it to disable it temporarily.
5. Click “Apply” and then “OK” to save the changes.
6. Restart your computer for the changes to take effect.
By disabling your antivirus software temporarily, you can troubleshoot your Windows 7 system recovery failure without any interference. Remember to re-enable your antivirus software once you have resolved the issue.
If you continue to experience system recovery failure, it may be necessary to contact technical support or seek assistance from a professional computer technician.
Check and Adjust System Protection Settings
1. Open the Control Panel by clicking the Start button and selecting Control Panel from the menu.
2. In the Control Panel, click on System and Security.
3. Under the System and Security section, click on System.
4. In the System window, click on the System Protection link on the left-hand side.
5. A System Properties window will open. Here, you can see the available drives on your computer.
6. Select the drive for which you want to check or adjust the system protection settings.
7. Click on the Configure button.
8. In the next window, you can adjust the system protection settings for the selected drive.
9. To enable system protection, select the “Turn on system protection” option.
10. Use the slider to specify how much disk space you want to allocate for system restore points.
11. Click on Apply and then click OK to save the changes.
12. If you want to create a system restore point manually, click on the Create button in the System Properties window.
13. Enter a description for the restore point and click Create.
14. To delete older restore points and free up disk space, click on the Delete button in the System Properties window.
Running System Restore from Safe Mode
1. Restart your computer and tap the F8 key repeatedly until the Advanced Boot Options menu appears.
2. Use the arrow keys to select “Safe Mode” and press Enter.
3. Once in Safe Mode, click the Start button and type “System Restore” in the search box.
4. In the search results, click on “System Restore” to open the System Restore wizard.
5. Follow the on-screen instructions to choose a restore point and initiate the restoration process.
6. After the restoration is complete, restart your computer in normal mode to see if the issue has been resolved.
Running System Restore from Safe Mode can help resolve Windows 7 System Recovery failures by allowing you to restore your computer to a previous state. This can be particularly useful if you have recently installed a new program or made changes to your system that have caused issues.
By accessing Safe Mode, you can bypass any potential conflicts or errors that may be preventing System Restore from running in normal mode. This allows you to perform the restoration process without interference, increasing the chances of a successful recovery.
Remember to choose a restore point that is before the issue started occurring. System Restore creates restore points automatically when significant changes are made to your system, such as installing new software or drivers. Selecting the most appropriate restore point can help ensure that the problematic changes are undone.
After the restoration process is complete, it is recommended to restart your computer in normal mode to verify whether the issue has been resolved. If the problem persists, you may need to consider other troubleshooting methods or seek further assistance.
Configure Disk Space Usage for System Restore
1. Click on the Start button and type “System Restore” in the search bar. Press Enter to open the System Restore window.
2. In the System Restore window, click on “Configure” to adjust the disk space usage.
3. A new window will open, showing the current disk space usage allocated for System Restore. To change the amount of disk space, move the slider to the desired percentage of your hard drive’s capacity. Keep in mind that allocating more disk space will allow for more restore points to be saved, but it will also occupy more storage space.
4. Once you have adjusted the disk space usage, click on the “Apply” button to save the changes.
By configuring the disk space usage for System Restore, you can ensure that enough space is allocated to store restore points without unnecessarily occupying too much of your hard drive’s capacity. This can help in fixing system recovery failures and restoring your Windows 7 system to a previous working state.
Initiating a Clean Boot Sequence
To initiate a clean boot sequence in Windows 7, follow these steps:
1. Press the Windows key + R to open the Run dialog box.
2. Type “msconfig” and press Enter to open the System Configuration utility.
3. In the System Configuration window, go to the “General” tab.
4. Under the “Selective startup” section, uncheck the box next to “Load startup items“.
5. Check the box next to “Load system services” and “Use original boot configuration“.
6. Go to the “Services” tab and check the box next to “Hide all Microsoft services“.
7. Click on the “Disable all” button to disable all non-Microsoft services.
8. Click on the “Apply” button and then click “OK” to save the changes.
9. When prompted to restart the computer, click “Restart“.
This will initiate a clean boot sequence in Windows 7, which helps identify and troubleshoot any issues that may be caused by startup items or non-Microsoft services. By disabling these items, you can determine if they are causing conflicts or problems with your system.
If you encounter any issues or need further assistance, you can refer to the Microsoft Knowledge Base or consult with a professional for support.
Using sfc to Repair System Files
To repair system files in Windows 7 using sfc, follow these steps:
1. Open the Command Prompt as an administrator. You can do this by searching for “Command Prompt” in the Start menu, right-clicking on it, and selecting “Run as administrator”.
2. In the Command Prompt window, type “sfc /scannow” and press Enter. This command will initiate the System File Checker (sfc) tool to scan for and repair any corrupted system files.
3. Wait for the scan to complete. This may take some time, so be patient. The sfc tool will automatically replace any corrupted files it finds with the correct versions from the Windows system image.
4. Once the scan is finished, you will see a message indicating whether any corrupted files were found and repaired. If no issues were found, you can close the Command Prompt window.
5. If the sfc tool was unable to repair all the corrupted files, you may need to perform additional troubleshooting steps or consider using other tools to fix the issue.
By using the sfc tool, you can easily repair system files in Windows 7 and restore the stability and performance of your operating system.
Installing Required Hotfixes
To fix a failed Windows 7 system recovery, you may need to install required hotfixes. Follow these steps to do so:
1. Identify the specific hotfixes needed for your system recovery. You can find a list of available hotfixes on the Microsoft website or in the Windows Knowledge Base.
2. Download the necessary hotfixes from the Microsoft website. Make sure you select the correct version (32-bit or 64-bit) of the hotfixes that match your Windows 7 installation.
3. Once the hotfixes are downloaded, locate the downloaded files on your computer.
4. Right-click on each hotfix file and select “Run as administrator” from the context menu.
5. Follow the on-screen instructions to install each hotfix. You may be prompted to restart your computer after each installation.
6. After installing all the required hotfixes, restart your computer if necessary.
7. Retry the system recovery process that previously failed. With the hotfixes installed, the system recovery should now complete successfully.
Registry and File Information
![]()
| Registry and File Information |
|---|
| Problem: System recovery failed on Windows 7 |
| Solution: Fixing registry and file issues |
| Steps: |
| 1. Boot the computer using a Windows 7 installation disk. |
| 2. Select the language and keyboard layout, then click “Next”. |
| 3. Click on “Repair your computer”. |
| 4. Select the operating system you want to repair, and click “Next”. |
| 5. Choose “Command Prompt” from the System Recovery Options. |
| 6. In the Command Prompt, run the following commands: |
a) chkdsk /f /r |
b) sfc /scannow |
c) dism /online /cleanup-image /restorehealth |
| 7. Restart the computer and try running system recovery again. |
Additional Support and Information
- Check for hardware issues: Ensure that all hardware components are properly connected and functioning correctly.
- Update drivers: Make sure all device drivers are up to date to avoid compatibility issues.
- Run a virus scan: Perform a thorough scan of your system to eliminate any potential malware or viruses that may be causing the recovery failure.
- Free up disk space: Remove unnecessary files and programs to ensure sufficient disk space for the recovery process.
- Disable startup programs: Temporarily disable any startup programs that may interfere with the recovery process.
- Perform a clean boot: Start Windows with minimal startup programs and services to avoid any conflicts during recovery.
- Check system files: Use the System File Checker tool to scan and repair corrupted system files.
- Reset BIOS settings: Restore the BIOS settings to default to eliminate any misconfigurations that could be causing the recovery failure.
- Try alternate recovery options: Explore other recovery methods such as using installation media or contacting technical support for further assistance.
- Backup important data: Prioritize backing up your important files and documents to prevent data loss during the recovery process.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I fix a failed System Restore?
To fix a failed System Restore, you can try the following steps:
– Use System Restore from Command Prompt.
– Use System Restore from Advanced Options.
– Use System Restore in Safe Mode.
– Disable your antivirus software.
– Rule out conflicts with third-party applications.
– Run the CHKDSK command.
– Run an SFC or DISM scan.
– Try using another system restore point.
How do I recover Windows 7 not booting?
To recover Windows 7 not booting, you can access the Advanced Boot Options menu by tapping the F8 key during startup. Select “Repair Your Computer” and then choose System Restore to fix the issue. Wait for the computer to restart without interrupting the process.
How do I force Windows 7 into recovery mode?
To force Windows 7 into recovery mode, press and hold the F8 key as your computer restarts, before the Windows logo appears.
How do I fix System Restore on Windows 7?
To fix System Restore on Windows 7, restart your computer and press and hold the F8 key before the Windows logo appears. Then, select “Repair Your Computer” from the Advanced Boot Options menu. Follow the prompts to select your language settings and click Next.

