Are you struggling with high memory usage on your Windows 10/11 Task Manager? Learn effective solutions to address this issue.
Understanding High Memory Usage
If you’re experiencing high memory usage on your Windows 10 or 11 Task Manager, there are a few steps you can take to fix the issue.
First, check for any malware or viruses on your computer. Use antivirus software to scan your system and remove any threats that may be causing the high memory usage.
Next, check your task manager to see which processes are using the most memory. You can do this by pressing Ctrl + Shift + Esc and clicking on the “Memory” tab. Identify any processes that are using a significant amount of memory and consider closing or uninstalling them if they are not necessary.
Another potential cause of high memory usage is memory paging. This is when your computer uses the hard disk drive or solid-state drive as additional memory when the RAM is full. To optimize memory usage, you can adjust the size of the virtual memory or increase the amount of RAM in your system if possible.
Additionally, you can try defragmenting your hard drive or using a tool like EaseUS Partition Master to repartition your disk space. This can help improve overall system performance and reduce memory usage.
Symptoms and Causes of High Memory Usage
- Identify the Symptoms of High Memory Usage
- Slow performance and system lag
- Unresponsive or slow applications
- Frequent freezing or crashing
- Excessive disk usage
- Determine the Causes of High Memory Usage
- Memory leaks in specific applications
- Background processes consuming excessive memory
- Malware or viruses
- Incompatible or outdated device drivers
- Insufficient RAM
Checking Your Computer’s Memory Usage
To check your computer’s memory usage on Windows 10/11 Task Manager, follow these steps:
1. Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc to open the Task Manager.
2. Click on the “Performance” tab at the top.
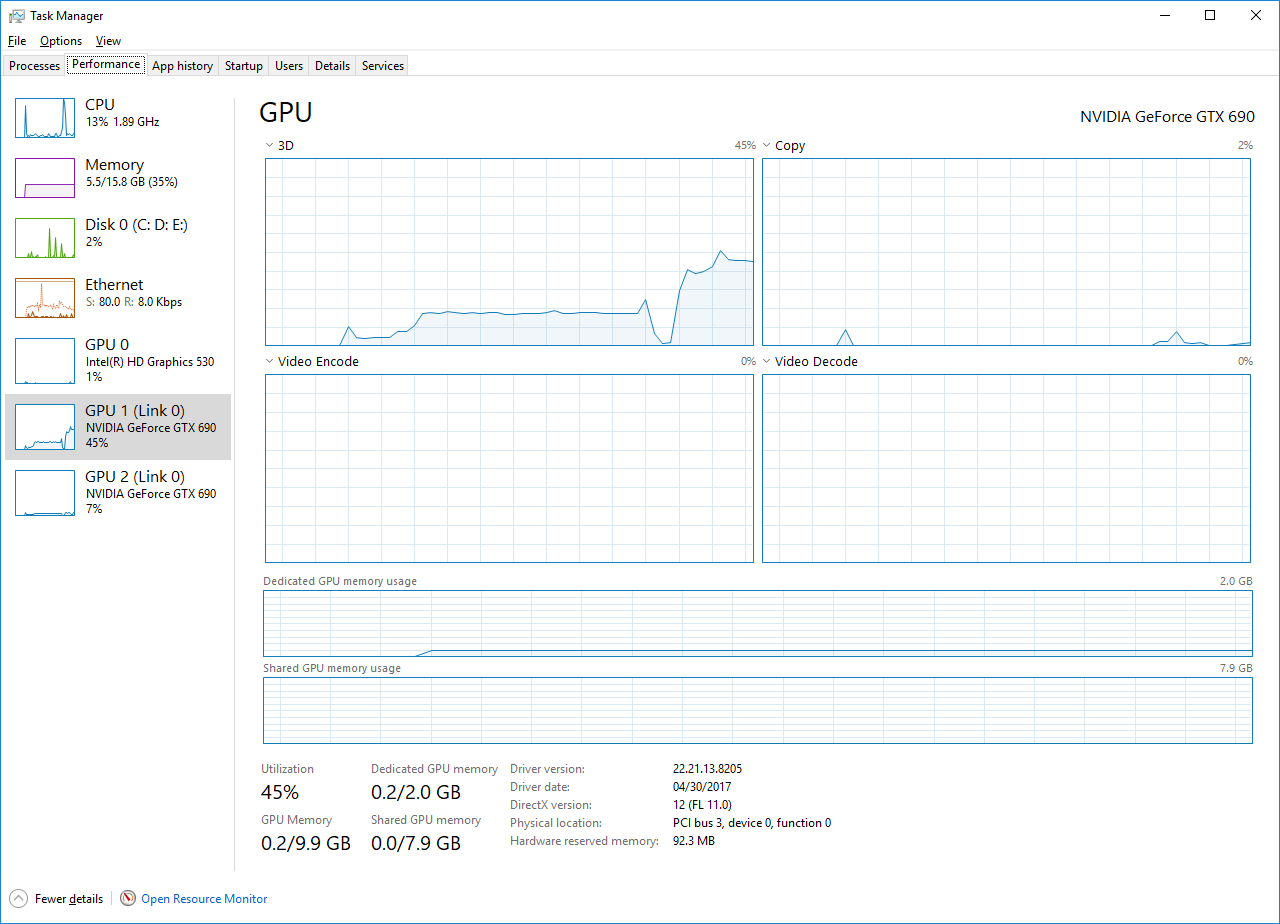
3. In the left-hand panel, click on “Memory” to view the memory usage details.
4. Here, you can see the total amount of memory (RAM) being used by your computer.
5. You can also view the percentage of memory being utilized and the amount of available memory.
6. To sort the processes by memory usage, click on the “Memory” column header.
7. You can identify memory-hungry processes by looking at the “Memory (Private Working Set)” column.
8. If you want to free up memory, you can right-click on a process and select “End Task”.
9. Additionally, you can open the Resource Monitor by clicking on “Open Resource Monitor” at the bottom of the Task Manager.
10. The Resource Monitor provides more detailed information about the memory usage of individual processes.
Closing Unnecessary Programs and Applications
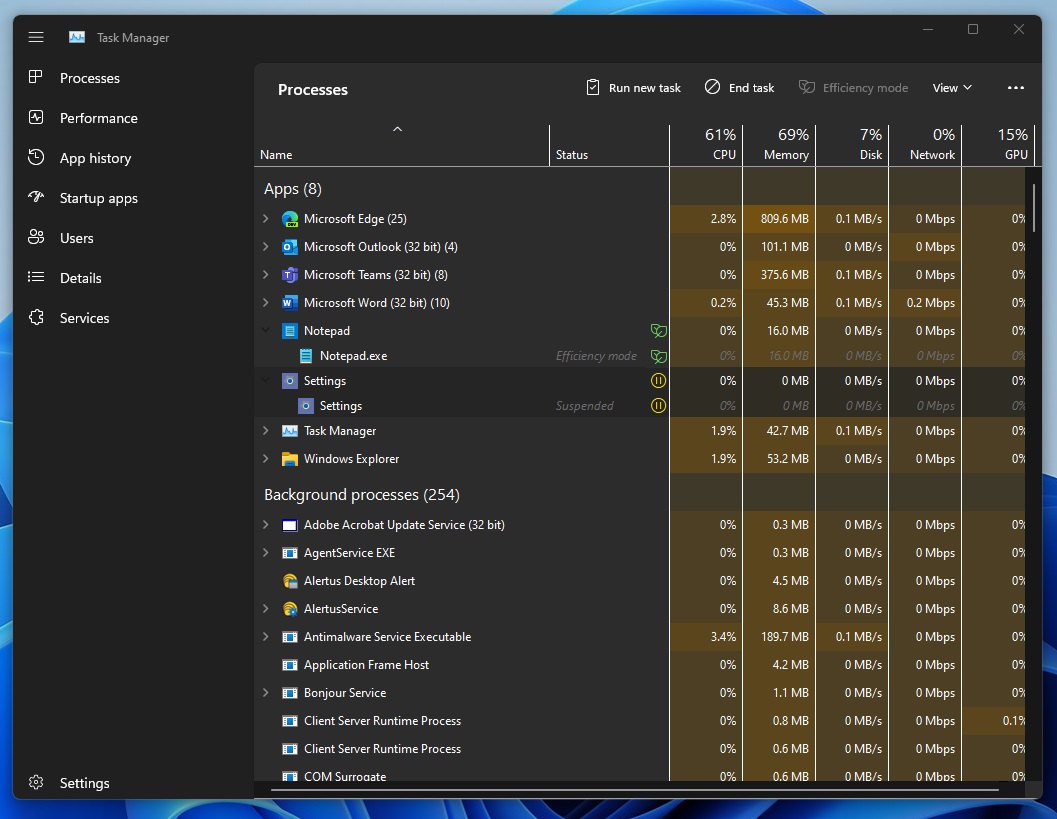
1. Open the Task Manager by pressing Ctrl+Shift+Esc.
2. In the Task Manager window, go to the “Processes” or “Details” tab.
3. Look for programs or applications that are using a significant amount of memory.
4. Right-click on the program or application and select End Task or End Process.
5. Repeat this process for any other unnecessary programs or applications that are using excessive memory.
6. You can also check the “Startup” tab in the Task Manager to disable any programs that automatically start when your computer boots up.
7. After closing unnecessary programs, check if the high memory usage issue is resolved.
Closing unnecessary programs and applications can free up memory and improve your computer’s performance. It is also a good practice to regularly check your startup programs and disable any unnecessary ones to prevent high memory usage in the future.
Disabling Startup Programs
To disable startup programs on Windows 10/11 Task Manager and fix high memory usage issues, follow these steps:
1. Open Task Manager by pressing Ctrl + Shift + Esc or right-clicking on the taskbar and selecting “Task Manager” from the context menu.
2. In the Task Manager window, click on the “Startup” tab.
3. You will see a list of programs that launch automatically when you start your computer. To disable a program, right-click on it and select “Disable” from the context menu.
4. Disable any unnecessary startup programs that might be causing high memory usage. Be cautious and only disable programs that you recognize and don’t need to run at startup.
5. Restart your computer for the changes to take effect.
Disabling startup programs can help improve computer performance by reducing the amount of memory and CPU resources used during startup. It can also help prevent unnecessary programs from running in the background, freeing up resources for other tasks.
Adjusting Virtual Memory Settings
To adjust virtual memory settings on Windows 10/11 Task Manager, follow these steps:
1. Open Task Manager by pressing Ctrl+Shift+Esc or right-clicking the taskbar and selecting “Task Manager.”
2. In Task Manager, click on the “Performance” tab.
3. Under the “Performance” tab, click on “Memory” in the left-hand menu.
4. In the “Physical Memory” section, click on “Open Resource Monitor” at the bottom.
5. In the Resource Monitor window, go to the “Memory” tab.
6. Click on the “Commit” column to sort the processes by memory usage.
7. Identify the processes that are using a large amount of memory.
8. Right-click on the process and select “Properties.”
9. In the properties window, go to the “Memory” tab.
10. Check the “Automatically manage paging file size for all drives” option if it’s not already checked.
11. If you want to manually adjust the virtual memory settings, uncheck the option mentioned above.
12. Click on “Custom size” and enter the desired initial and maximum size for the virtual memory.
13. Click “Set” and then “OK” to save the changes.
14. Restart your computer for the changes to take effect.
Optimizing Hard Drive Performance

To optimize hard drive performance and fix high memory usage issues on Windows 10/11 Task Manager, follow these steps:
1. Check for viruses: Run a thorough scan using reliable antivirus software to ensure your system is not infected.
2. Manage startup programs: Open Task Manager (Ctrl+Shift+Esc), go to the “Startup” tab, and disable unnecessary programs from starting up with your computer.
3. Clear memory cache: In Task Manager, go to the “Processes” tab, select any unnecessary processes, and click “End Task” to clear up memory usage.
4. Optimize virtual memory: Open the Windows Control Panel, search for “Advanced System Settings,” go to the “Advanced” tab, and click on “Settings” under the “Performance” section. In the new window, go to the “Advanced” tab, click on “Change” under the “Virtual memory” section, and select “System managed size” or set a custom size for better performance.
5. Defragment your hard drive: Open File Explorer, right-click on the hard drive, go to “Properties,” select the “Tools” tab, and click on “Optimize.” This will rearrange fragmented data and improve disk performance.
6. Update your drivers: Visit your computer manufacturer’s website or use driver update software to ensure all your drivers are up to date.
7. Free up disk space: Use Disk Cleanup (search for it in the Start menu) to remove unnecessary files and free up disk space.
Managing Windows Services and Registry Settings
- Stop unnecessary Windows services
- Disable startup programs
- Adjust virtual memory settings
- Clear temporary files and folders
- Update device drivers
- Run a full system scan for malware
- Disable unnecessary visual effects
- Disable unnecessary background processes
- Optimize power settings
- Perform a clean boot
- Modify registry settings
Addressing Software and Virus Issues
If you’re experiencing high memory usage on your Windows 10 or 11 Task Manager, there are a few steps you can take to address the issue. First, check for any software or virus issues that might be causing the problem. Run a full virus scan using a reliable antivirus program to ensure your computer is free from any malware.
Next, check your computer’s memory usage in the Task Manager. Look for any processes or applications that are using a large amount of memory. If you find any, try closing those applications or processes to free up memory.
If the high memory usage issue persists, you can try defragmenting your hard disk drive or using a disk partitioning tool like EaseUS Partition Master to optimize your disk storage. Additionally, you can try cleaning up your Windows Registry using a trusted software program.
If none of these steps resolve the issue, you might consider upgrading your computer’s memory or switching to a solid-state drive (SSD) for better performance.
Enhancing System Performance and Capacity
To enhance system performance and capacity on Windows 10/11 Task Manager and fix high memory usage issues, follow these steps:
1. Identify resource-hungry processes: Open Task Manager by pressing Ctrl + Shift + Esc and go to the “Processes” tab. Look for processes consuming a large amount of memory.
2. End unnecessary processes: Right-click on resource-intensive processes and select “End Task”. Be cautious not to terminate essential system processes.
3. Disable startup programs: Open Task Manager, go to the “Startup” tab, and disable unnecessary programs from starting up with your computer.
4. Check for malware: Run a full scan using reliable antivirus software to detect and remove any malware that might be causing high memory usage.
5. Adjust virtual memory settings: Press Windows key + R, type “sysdm.cpl”, and press Enter. Go to the “Advanced” tab, click on “Settings” under the “Performance” section. In the “Virtual memory” tab, click “Change” and uncheck “Automatically manage paging file size for all drives”. Set a custom size or let Windows manage it.
6. Update drivers and Windows: Outdated drivers can cause high memory usage. Update your drivers by going to the manufacturer’s website or using a reputable driver updater software. Also, make sure your Windows operating system is up to date.
7. Perform a disk cleanup: Press Windows key + S, type “Disk Cleanup”, and select the utility. Choose the drive you want to clean up and select the file types to delete. Click “OK” to start the cleanup process.
8. Disable unnecessary visual effects: Press Windows key + X, select “System”, go to the “Advanced system settings” on the left panel, click on the “Settings” button under the “Performance” section. Choose the “Adjust for best performance” option or manually deselect unnecessary visual effects.
9. Upgrade your hardware: If your computer’s hardware is outdated or insufficient, consider upgrading your RAM or replacing your hard drive with a solid-state drive (SSD) for better performance.
Recovering from Memory Usage Issues
If you’re experiencing high memory usage on your Windows 10/11 Task Manager, there are a few steps you can take to recover from this issue. First, check for any computer viruses that may be causing the problem. Use a reliable antivirus software to scan your system and remove any threats.
Next, check your computer’s random-access memory (RAM) and make sure it’s not being overloaded. Close any unnecessary programs or processes that are using up a lot of memory.
You can also try adjusting your computer’s memory paging settings. Open the System Properties window by pressing the Windows key + Pause/Break, then click on “Advanced system settings.” Under the Performance section, click on “Settings” and go to the “Advanced” tab. Click on “Change” in the Virtual Memory section and adjust the paging file size accordingly.
Additionally, you can try cleaning up your computer’s disk storage by deleting unnecessary files or using disk cleanup tools. Defragmenting your hard drive can also help improve memory usage.
If the issue persists, you may need to troubleshoot specific applications or processes that are causing high memory usage. Use the Task Manager to identify these processes and try updating or reinstalling the associated software.
Preventive Measures and Best Practices
- Close unnecessary programs and processes:
- Open Task Manager by pressing Ctrl+Shift+Esc
- Select the Processes tab
- Identify and select any unnecessary programs or processes
- Click on the End Task button
- Update your operating system and drivers:
- Press the Windows key and type “Windows Update”
- Select Windows Update settings
- Click on Check for updates and install any available updates
- Visit the manufacturer’s website to update drivers for your hardware
- Scan for malware and viruses:
- Install and run a reputable antivirus or antimalware program
- Perform a full system scan
- Follow the instructions to remove any detected threats
- Optimize your computer’s performance:
- Press the Windows key and type “Performance”
- Select Adjust the appearance and performance of Windows
- In the Visual Effects tab, choose Adjust for best performance or customize the settings according to your preference
- Click Apply and OK to save the changes
- Manage startup programs:
- Press Ctrl+Shift+Esc to open Task Manager
- Select the Startup tab
- Disable any unnecessary programs from starting up with your computer
- Right-click on the program and choose Disable
F.A.Q.
Why is my memory so high in Task Manager?
Your memory usage may be high in Task Manager due to several possible reasons. One possibility is that you have a large program or game running that is consuming a significant amount of system RAM. Another potential reason could be the presence of malware on your device, which can cause high memory usage.
Why is my computer memory so full?
Your computer memory is full because of the number of applications and files you have opened. To free up memory, close any unnecessary programs and files. Additionally, you can check memory usage and performance in Task Manager (CTRL+ALT+Del) and run a virus scan to ensure there are no unusual activities affecting your computer’s memory.
Is 100% memory usage bad?
100% memory usage is not necessarily bad, but it can indicate a potential issue.
How do I free up memory in Task Manager?
To free up memory in Task Manager, you can open Task Manager, navigate to the Processes tab, identify the programs or software consuming excessive memory and CPU usage, and then select and end those tasks to stop them from running on your computer.

