Are you stuck in a never-ending loop of automatic repair on your Windows 8? Find out how to fix it in this tutorial.
Understanding the Startup Repair Loop

If you find yourself stuck in a startup repair loop on Windows 8, don’t worry, there is a fix. Here’s a tutorial to help you get out of this frustrating cycle.
1. Start by restarting your computer and tapping the F8 key repeatedly during the boot process. This will take you to the Advanced Boot Options menu.
2. From the menu, select Safe Mode and press enter. This will boot your computer into a limited version of Windows, allowing you to troubleshoot the issue.
3. Once in Safe Mode, open the Control Panel and navigate to the System and Security section.
4. In System and Security, click on Action Center and then select Recovery .
5. Under the Advanced Recovery Tools section, click on Open System Restore .
6. Follow the prompts to restore your computer to a previous working state. This will undo any recent changes that may have caused the startup repair loop.
7. If System Restore doesn’t solve the issue, you can try running the CHKDSK utility. Open the command prompt as an administrator and type chkdsk C: /f and press enter. This will scan and repair any errors on your hard drive.
8. If all else fails, you can try booting from a Windows installation disk or a bootable USB flash drive and perform a system repair.
Common Causes of the Repair Loop
- Restart your computer.
- As soon as the computer starts booting, press the F8 key repeatedly.
- On the Advanced Boot Options screen, use the arrow keys to select Disable automatic restart on system failure.
- Press Enter to save the changes and continue booting your computer.
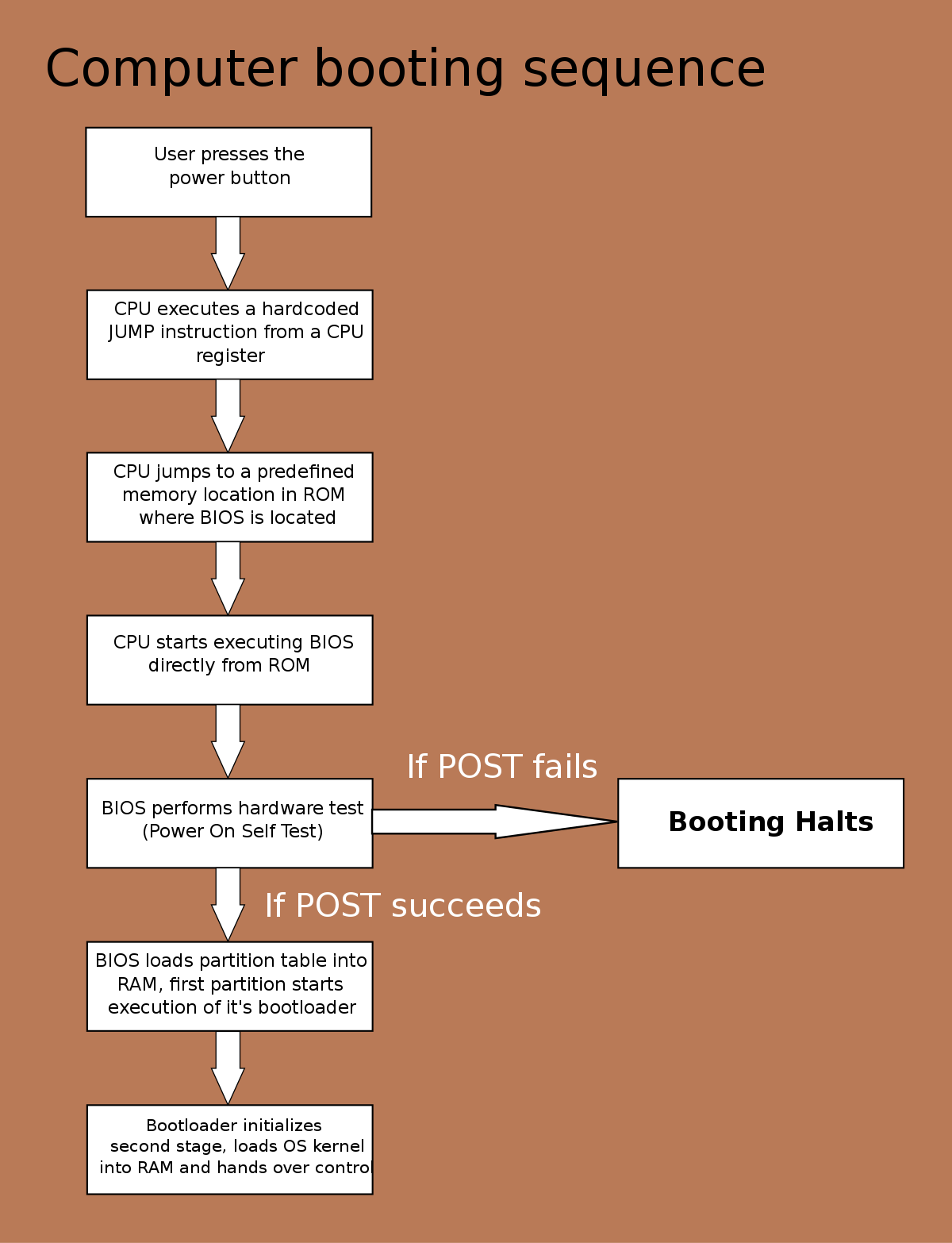
Method 2: Run Startup Repair
- Insert your Windows installation disc or recovery drive.
- Restart your computer.
- Press any key to boot from the installation media when prompted.
- Select your language preferences and click on Next.
- Click on Repair your computer.
- Select Troubleshoot from the options.
- Click on Advanced options.
- Click on Startup Repair.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the repair process.
- Restart your computer.
Method 3: Use System Restore
- Insert your Windows installation disc or recovery drive.
- Restart your computer.
- Press any key to boot from the installation media when prompted.
- Select your language preferences and click on Next.
- Click on Repair your computer.
- Select Troubleshoot from the options.
- Click on Advanced options.
- Click on System Restore.
- Select a restore point and follow the on-screen instructions to restore your system.
- Restart your computer.
Method 4: Use Command Prompt
- Insert your Windows installation disc or recovery drive.
- Restart your computer.
- Press any key to boot from the installation media when prompted.
- Select your language preferences and click on Next.
- Click on Repair your computer.
- Select Troubleshoot from the options.
- Click on Advanced options.
- Click on Command Prompt.
- Enter the necessary commands to fix the issue, such as bootrec /fixmbr or chkdsk /r.
- Restart your computer.
Method 5: Refresh or Reset Your PC
- Insert your Windows installation disc or recovery drive.
- Restart your computer.
- Press any key to boot from the installation media when prompted.
- Select your language preferences and click on Next.
- Click on Repair your computer.
- Select Troubleshoot from the options.
- Click on Advanced options.
- Click on Refresh your PC to keep your files or Reset your PC to remove everything.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the process.
- Restart your computer.
Accessing Recovery Tools
To access recovery tools on Windows 8 and fix the automatic repair loop, follow these steps:
1. Restart your computer and press the Arrow keys to navigate to the Advanced options screen.
2. Select Troubleshoot and then choose Advanced options.
3. From the list of options, click on Startup Repair to automatically fix any startup issues.
4. If the automatic repair doesn’t work, go back to the Advanced options screen and select Command Prompt.
5. In the command prompt, type “bootrec /fixmbr” to repair the Master Boot Record.
6. Next, type “bootrec /fixboot” to fix the bootloader.
7. If you’re still experiencing issues, try running “chkdsk /f” to check and repair any disk errors.
8. Another option is to use the “sfc /scannow” command to scan and repair system files.
9. If all else fails, you can use a system image or recovery drive to restore your computer to a previous working state.
Running Chkdsk to Fix Boot Volume Issues
To fix boot volume issues in Windows 8, you can run Chkdsk. This utility checks for and repairs any disk errors that may be causing the automatic repair loop. Here’s how to do it:
1. Restart your computer and boot from a Windows installation disc or a USB flash drive with a Windows 8 ISO image.
2. On the Windows Setup screen, choose your language preferences and click “Next.”
3. Click “Repair your computer” at the bottom left corner of the screen.
4. Select “Troubleshoot” > “Advanced options” > “Command Prompt.”
5. In the Command Prompt window, type “chkdsk C: /f” and press Enter. Replace “C:” with the drive letter of your Windows installation if it’s different.
6. Chkdsk will scan the drive for errors and repair them if necessary. This process may take some time.
7. Once Chkdsk finishes, type “exit” and press Enter to close the Command Prompt window.
8. Restart your computer and see if the boot volume issues have been resolved.
Running Chkdsk can help fix disk-related problems that may be causing the automatic repair loop in Windows 8.
Disabling Automatic Restart Feature
To disable the Automatic Restart feature in Windows 8, follow these steps:
1. Press the Windows key + R to open the Run dialog box.
2. Type “sysdm.cpl” and press Enter to open the System Properties window.
3. In the System Properties window, go to the “Advanced” tab.
4. Under the “Startup and Recovery” section, click on the “Settings” button.
5. In the Startup and Recovery window, uncheck the box that says “Automatically restart” under the System Failure section.
6. Click “OK” to save the changes and close the windows.
Disabling the Automatic Restart feature can be helpful when troubleshooting issues such as the Windows 8 Automatic Repair Loop. This feature prevents the computer from continuously restarting, allowing you to view any error messages or perform necessary actions to fix the problem.
Booting into Safe Mode for Troubleshooting
Booting into Safe Mode can be a useful troubleshooting step when dealing with issues on your Windows 8 system. Safe Mode allows you to load the operating system with minimal drivers and services, making it easier to identify and resolve problems.
To boot into Safe Mode on Windows 8, follow these steps:
1. Press the “Windows key + R” to open the Run dialog box.
2. Type “msconfig” and press Enter to open the System Configuration window.
3. In the System Configuration window, go to the “Boot” tab.
4. Check the box next to “Safe boot” and select “Minimal“.
5. Click “Apply” and then “OK” to save the changes.
6. When prompted to restart your computer, click “Restart”.
Once your computer restarts, it will boot into Safe Mode. In Safe Mode, you can troubleshoot issues such as software conflicts, driver problems, or malware infections. You can also perform tasks like running antivirus scans, updating drivers, or uninstalling problematic software.
Remember that Safe Mode only loads essential drivers and services, so some features may be unavailable. If you need to access the internet or use specific programs that are not available in Safe Mode, you may need to boot back into normal mode.
Safe Mode can be a valuable tool for resolving issues on your Windows 8 system.
Utilizing Bootrec to Repair Boot Issues
To fix boot issues in Windows 8, you can use the Bootrec tool. Bootrec is a command-line tool that can repair the Master Boot Record (MBR), boot sector, and BCD (Boot Configuration Data). Here’s a step-by-step tutorial on how to use Bootrec to fix boot issues:
1. Boot your computer using a Windows installation disc or a system repair disc.
2. Select your language preferences and click “Next.”
3. Click “Repair your computer” at the bottom left corner of the screen.
4. Select the operating system you want to repair and click “Next.”
5. In the System Recovery Options menu, click “Command Prompt.”
6. Type “bootrec /fixmbr” and press Enter.
This command repairs the Master Boot Record.
7. Type “bootrec /fixboot” and press Enter.
This command repairs the boot sector.
8. Type “bootrec /rebuildbcd” and press Enter.
This command rebuilds the BCD.
9. Restart your computer and check if the boot issue is resolved.
By using Bootrec, you can fix boot issues caused by corrupted or missing system files, a damaged MBR or boot sector, or other similar problems. It’s a powerful tool that can help you get your Windows 8 system up and running again.
Restoring Windows with System Restore
To restore Windows using System Restore, follow these steps:
1. Boot your computer and press the F8 key repeatedly until the Advanced Boot Options menu appears.
2. Use the arrow keys to select “Repair Your Computer” and press Enter.
3. Select your preferred language and click “Next.”
4. Enter your administrator username and password, if prompted, and click “OK.”
5. On the System Recovery Options screen, click “System Restore.”
6. Select a restore point from the list and click “Next.”
7. Review the selected restore point and click “Finish” to start the restoration process.
8. Wait for the process to complete, and then click “Restart” to reboot your computer.
System Restore will revert your computer’s settings and system files to a previous state, potentially resolving issues such as an automatic repair loop or software conflicts.
Note: System Restore will not affect your personal files, but it is still recommended to back up any important data before proceeding.
Rebuilding BCD and Checking Boot Priority
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Step 1 | Start your computer and press the F8 key repeatedly until the Advanced Boot Options menu appears. |
| Step 2 | Select “Repair Your Computer” and press Enter. |
| Step 3 | Choose your language preferences and click “Next”. |
| Step 4 | Click on “Troubleshoot”. |
| Step 5 | Click on “Advanced options”. |
| Step 6 | Select “Command Prompt”. |
| Step 7 | Type the following command and press Enter: bootrec /fixmbr |
| Step 8 | Type the following command and press Enter: bootrec /fixboot |
| Step 9 | Type the following command and press Enter: bootrec /rebuildbcd |
| Step 10 | Follow the on-screen prompts to select the Windows installation you want to repair and press Enter. |
| Step 11 | Restart your computer and check if the automatic repair loop issue is resolved. |
Addressing Corrupted Files and Registry Settings
In the Windows 8 Automatic Repair Loop Fix tutorial, we will guide you on how to address corrupted files and registry settings. If you find yourself stuck in an infinite loop of automatic repairs, follow these steps to resolve the issue.
First, reboot your computer and enter the Advanced Startup Options by pressing F8 or through the Windows Boot Manager. From there, select “Troubleshoot” and then “Advanced Options.”
Next, choose “Command Prompt” to access the command-line interface. In the command prompt, type “sfc /scannow” and hit enter to run the System File Checker. This tool will scan and repair any corrupted system files.
If the System File Checker doesn’t fix the issue, you can try resetting your PC to its default state. In the command prompt, type “rstrui.exe” and press enter to open the System Restore interface. Follow the on-screen instructions to restore your computer to a previous working state.
If these steps don’t resolve the problem, you may need to consider restoring your system from a system image or performing a clean installation of Windows 8.
Frequently Asked Questions
How to repair Windows 8.1 using Command Prompt?
To repair Windows 8.1 using Command Prompt, follow these steps:
1. Right click the Start button and choose Command Prompt (Admin).
2. In the command prompt window, type: dism /online /cleanup-image /restorehealth
3. Press Enter or paste the command by right clicking in the window and selecting Paste.
4. Wait for the process to finish.
How do I fix startup repair on Windows 8?
To fix startup repair on Windows 8, you can follow these steps:
– Click Start and then click the power button icon.
– Press and hold down the Shift key and then click Restart.
– Select Troubleshoot and go to Advanced Options.
– Choose Startup Repair and allow the process to complete.
– Finally, reboot your computer.
How do you fix an endless repair loop?
To fix an endless repair loop, you can try the following steps:
– Run Fixboot and Chkdsk Commands.
– Perform a System Scan in Safe Mode.
– Restore the Windows Registry.
– Disable the Automatic Repair Tool.
– Disable Early Launch Anti-Malware.
– Perform a Hard Reboot.
How do I fix the automatic repair loop in Windows 8?
To fix the automatic repair loop in Windows 8, you can try the following steps:
– Insert the Windows installation disc and restart the computer.
– Press any key to boot from the DVD.
– Select your keyboard layout.
– Click on “Repair your computer” at the Install now screen.
– Choose “Troubleshoot” and then click on “Advanced options”.
– Select “Startup Settings” and click on “Restart”.

